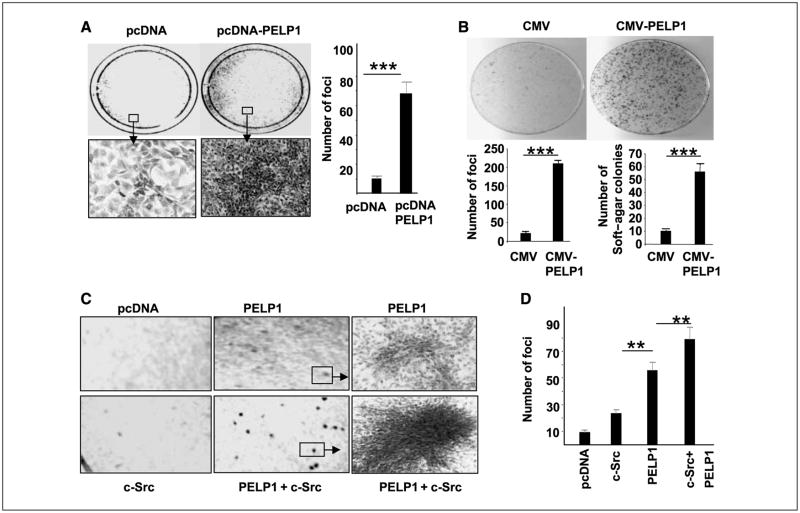
Figure 1.
PELP1 transforms NIH3T3 cells. A, pcDNA vector or pcDNA-PELP1 vector was transiently transfected into NIH3T3 cells, and focus formation was counted after 14 d. Bottom, representative morphologic characteristics of a transformed colony induced by PELP1. The number of transformed foci were counted in these plates, and the result was corrected for transfection efficiency by counting G418-resistant colonies (left). B, NIH3T3 cells were cotransfected with either CMV + pNeomycin plasmid or CMV-PELP1 + pNeomycin plasmid. G418 resistant colonies were selected, and transformation potential of pooled clones expressing CMV vector or PELP1 was analyzed for focus formation and soft-agar colony formation. C, NIH3T3 cells were transiently transfected with pcDNA, or c-Src, and/or c-Src + PELP1, and focus formation was recorded after 14 d. A representative portion from each plate is shown. D, quantitation of the focus formation observed in the plates.