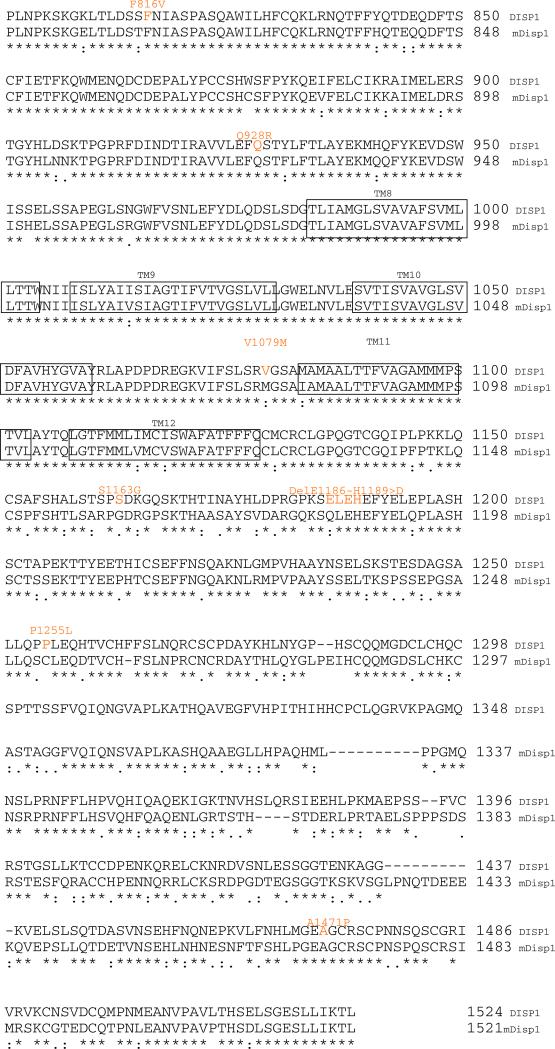
Fig. 1.
Protein alignment of human DISP1 and murine Disp1 proteins based on the Clustal W algorithm (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/clustalw2/index.html). Both of these vertebrate Disp are orthologs of Drosophila disp (not shown) are predicted to share a common topology with a core 12 membrane-spanning structure (each transmembrane element is boxed to indicate the membrane embedded amino acids) including the segment between boxed transmembrane regions (TM) 2–5 comprising the sterol-sensing domain. Key differences between genetic variants of the human and murine proteins are highlighted in orange (mis-sense or in-frame deletion) or red (truncating mutations)