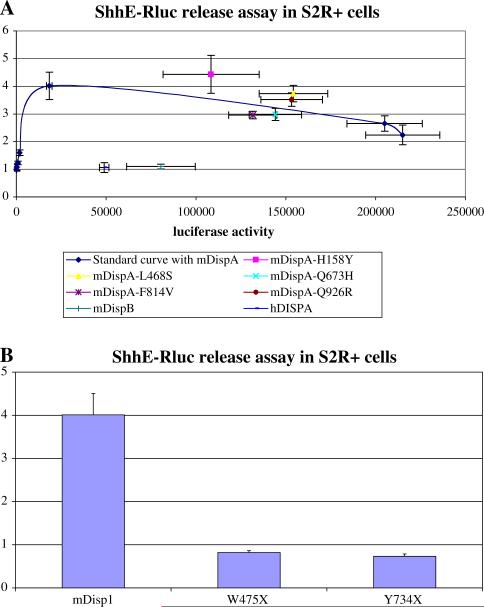
Fig. 2.
Determination of relative functional activity of genetic variants by assessment of the transporter function of Disp on a renilla-tagged Shh reporter in Drosophila S2R+ cells. a The standard dose–response curve with transfected murine DispA documents that increasing amounts of murine DispA (determined by measurement of the firefly luciferase activity on the X-axis) results in a maximum stimulation of ShhE-Rluc export of fourfold. In contrast, the murine DispB or the human DISPA fail to enhance ShhE-Rluc reporter export under these conditions (in spite of adequate expression of the N-firefly luciferase-tagged proteins). Five of the mis-sense changes incorporated within the murine DispA backbone cDNA could be studied; however, none of these variants appreciably affected the transporter-like function of the Disp test protein. b Normally, a bioactive murine Disp1 construct will enhance the export of the tagged Shh ligand by 4- to 10-fold (Ma et al. 2002). Both truncation mutations (murine construct versions mimicking W475X and Y734X) abrogate the ability of the Disp1 test molecule to influence ShhE-Rluc export. Values reported are the maximal release values obtained at a fixed input of Disp1 construct used in all three examples