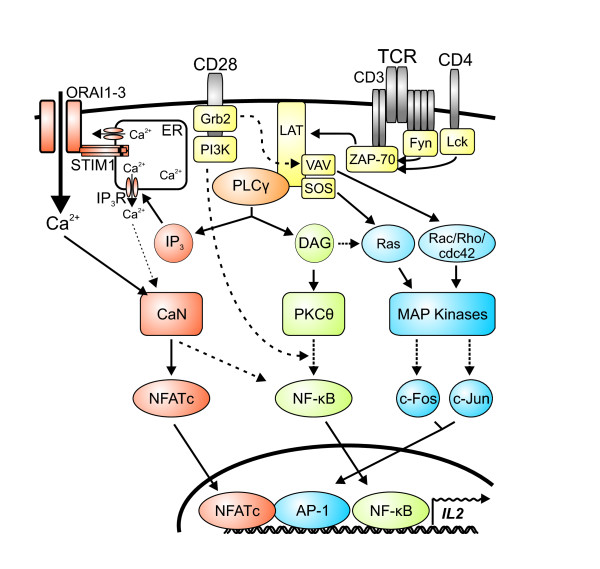
Figure 1.
Schematic overview about TCR-dependent signalling pathways. Engagement of TCRs and costimulatory CD28 receptors promote signalling cascades of kinases and adaptor proteins (yellow). They trigger pathways resulting in the activation of the transcription factors NFATc (red), NF-κB (green) and AP-1 (blue). These transcription factors cooperate with each other during the activation of several genes, e.g. IL-2. Of special interest for this review is the calcineurin-NFATc pathway: IP3, generated by PLCγ (orange) via cleavage of PIP2, binds to the IP3 receptor (IP3R) and causes the release of Ca2+ from the endoplasmatic reticulum (ER). This Ca2+ depletion is sensed by STIM1, which is directly coupled to the ORAI CRAC channels. Influx of extracellular Ca2+ into the cytosol activates calcineurin (CaN), leading to the dephosphorylation and nuclear translocation of NFATc. DAG: diacylglycerol; IP3: inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate; PIP2: phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate; PKCθ: protein kinase C theta; PLCγ: phospholipase C gamma.