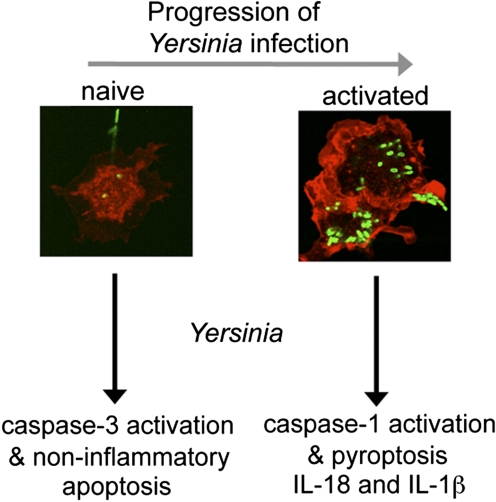
Figure 2.
Redirected cell death during host response to Yersinia infection. Initial interaction of Yersinia with naïve macrophages results in the activation of caspase-3 and induction of noninflammatory apoptosis (left). With additional bacterial replication, macrophage activation occurs as a result of TLR stimulation (or other yet-to-be-defined pathways), and interaction with Yersinia results in caspase-1 activation, maturation, and release of IL-1β and IL-18 and cell lysis with the release of inflammatory intracellular contents (right).