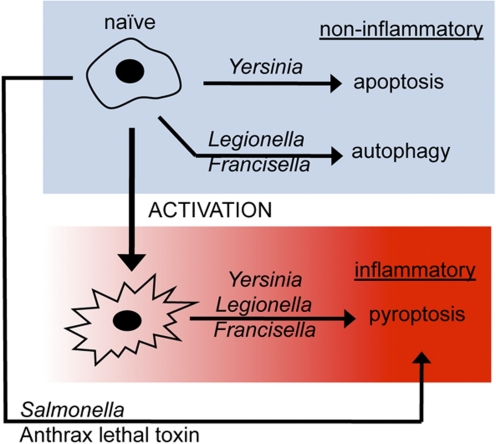
Figure 3.
Pyroptosis is a conserved effector pathway important in combating infection. The interaction of naïve macrophages with anthrax lethal toxin or Salmonella results in pyroptosis [51]; with Yersinia, noninflammatory apoptosis occurs but can be redirected to pyroptosis (see text for more details [20]); with Legionella [66] or Francisella [67] infection, noninflammatory autophagy occurs and transitions to pyroptosis. Physiological outcome is dictated by cell death mechanism; control is subject to influence by pathogen (ligands and virulence determinants translocated into host cell) and host (macrophage activation and redirected use of cell death pathway) [50].