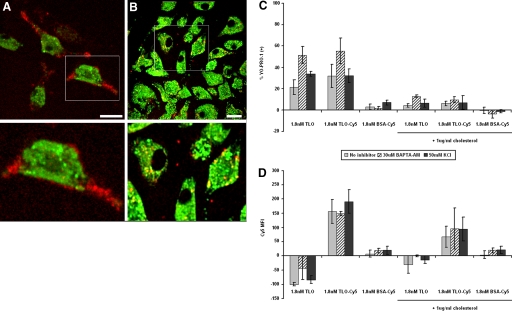
Figure 8.
TLO binding and pore formation still occur in the presence of inhibitors of IL-1β secretion. (A and B) Four-hour LPS-primed BMDM were labeled with LysoTracker™ Green dye (green) for intracellular tracking purposes and then treated with 1.8 nM TLO-Cy5 (red) inactivated with 1 μg/ml cholesterol or left untreated. BMDM were imaged by live cell microscopy to track active or cholesterol-inactivated TLO-Cy5 after addition. These midplane sections taken at 10 min post-treatment show that active toxin binds primarily to the surface of BMDM (A), and cholesterol-bound toxin is internalized by BMDM (B). The lower panels show magnifications of boxed cells displayed in the upper panels. Original white bar scales indicate a 10-μm length. (C and D) Four-hour LPS-primed BMDM were treated with no inhibitor (buffer only), 50 mM KCl, or 30 μM BAPTA-AM for 1 h, followed by addition of control (DTT-containing buffer), 1.8 nM TLO, 1.8 nM TLO-Cy5, or 1.8 nM BSA-Cy5 in the presence or absence of 1 μg/ml cholesterol for 5 min. BMDM were analyzed by flow cytometry for TLO-induced pore formation (YO-PRO-1 uptake; A) and TLO binding (Cy5 signal; B). BMDM bind to pore-inducing TLO-Cy5, but not control BSA-Cy5, in the absence of IL-1β inhibitors as well as in the presence of BAPTA-AM or KCl. Data represent mean ± sem for three independent experiments. Control background values were subtracted out from the data. MFI, Mean fluorescence intensity.