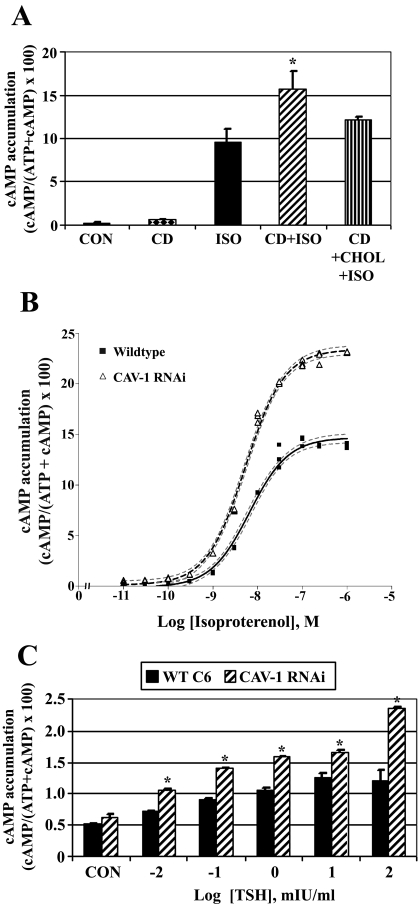
Fig. 3.
Disruption of lipid rafts/caveolae with cyclodextrin or caveolin knockdown increases βAR and TSHR-stimulated cAMP accumulation. Wild-type C6 cells were incubated with [2,8-3H]adenine for 18 h to label cellular ATP. A, cells were treated initially with ± 10 mM methyl-β-cyclodextrin (CD) for 30 min to disrupt lipid rafts/caveolae, or with CD followed by CD-cholesterol complexes (CD+CHOL) for 90 min to restore cholesterol to the cells. Intact cells were subsequently treated with 10 μM isoproterenol (ISO) for 30 min and [2,8-3H]cAMP accumulation was determined. Data presented are the means ± S.E.M. from six independent experiments performed in triplicate (n = 6). *, p < 0.05 versus ISO-treated cells. B, wild-type C6 cells or caveolin-1-stable knockdown cells (CAV-1 RNAi) were incubated with [2,8-3H]adenine for 18 h to label cellular ATP. Intact cells were treated with increasing concentrations of ISO for 30 min and [2,8-3H]cAMP accumulation was determined. Data are the means ± S.E.M. from a single dose-response experiment performed in triplicate with similar results observed in three independent experiments. C, wild-type C6 cells or CAV-1 RNAi cells were transiently transfected with human thyrotropin (TSH) receptor and 24 h later were incubated with [2,8-3H]adenine for 18 h to radioactively label cellular ATP. Intact cells were treated with increasing concentrations of TSH for 30 min, and [2,8-3H]cAMP accumulation was determined. Data are the means ± S.E.M. from three independent experiments. *, p < 0.05 versus WT C6 cells for each treatment group.