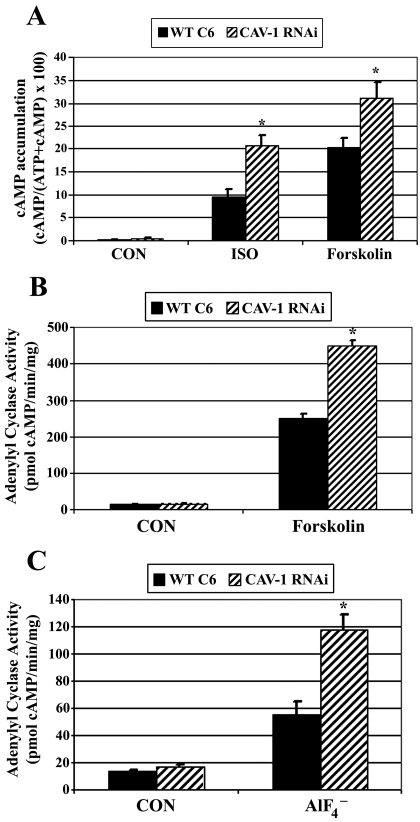
Fig. 4.
Caveolin knockdown increases forskolin- and fluoride-stimulated Gαs/adenylyl cyclase signaling. A, wild-type C6 cells (WT C6) or caveolin-1 stable knockdown cells (CAV-1 RNAi) were incubated with [2,8-3H]adenine for 18 h to label cellular ATP. Intact cells were treated with ± 10 μM isoproterenol (ISO) or 100 μM forskolin for 30 min, and [2,8-3H]cAMP accumulation was determined. Data presented are the means ± S.E.M. from six independent experiments performed in triplicate (n = 6). *, p < 0.05 versus WT C6 cells for each treatment group. B, adenylyl cyclase activity was determined in cell membranes isolated from WT C6 or CAV-1 RNAi cells. Membranes were incubated with ± 50 μM forskolin for 20 min [32P]cAMP was isolated and determined by scintillation counting, normalized to time and milligrams of membrane protein. Data presented are the means ± S.E.M. from a single experiment performed in triplicate and are representative of similar results observed in three independent experiments. C, adenylyl cyclase activity was determined in cell membranes isolated from WT C6 or CAV-1 RNAi cells. Membranes were incubated for 20 min with a reaction mixture including 32P-ATP and ± 10 mM sodium fluoride/20 μM aluminum chloride. [32P]cAMP was isolated and determined by scintillation counting, normalized to time and milligrams of membrane protein. Data presented are the means ± S.E.M. from an experiment performed in triplicate and is representative of similar results observed in four independent experiments.