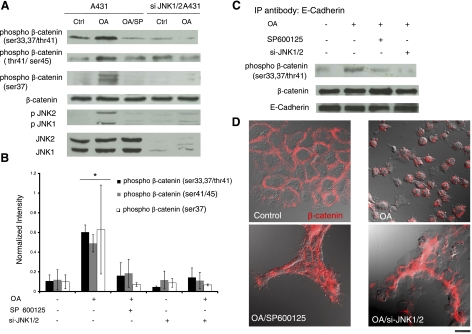
Figure 8.
JNK activation induces β-catenin phosphorylation and disruption of cell-cell adhesion. A431 cells were transduced with recombinant lentivirus encoding for EGFP and shRNA targeting JNK1/2. EGFP+ cells were sorted using flow cytometry and denoted as si-JNK1/2 A431 cells. Control or si-JNK1/2 A431 cells were treated with OA (500 nM) for 30 min in the presence or absence of SP600125 (10 μM) as indicated. SP600125 was added for 30 min before as well as during OA treatment. A) Cell lysates were subjected to Western blotting using 3 different antibodies against phosphor-β-catenin at Ser-33,37/Thr41, Thr41/Ser-45, or Ser-37, as well as p-JNK, total JNK, and total β-catenin. B) The band intensity of phosphor-β-catenin was determined using Kodak gel documentation software and normalized to total β-catenin. Data from 3 independent experiments were plotted as means ± se; n = 3. C) Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with an antibody against E-cadherin, and phosphor-β-catenin and total β-catenin were detected using Western blotting. E-cadherin served as a loading control. D) Immunostaining of control or si-JNK1/2 A431 cells for β-catenin (red) under the indicated conditions. Fluorescence and differential interference contrast images were overlaid to highlight β-catenin localization and cell morphology (view ×63). Scale bar = 20 μm.