Abstract
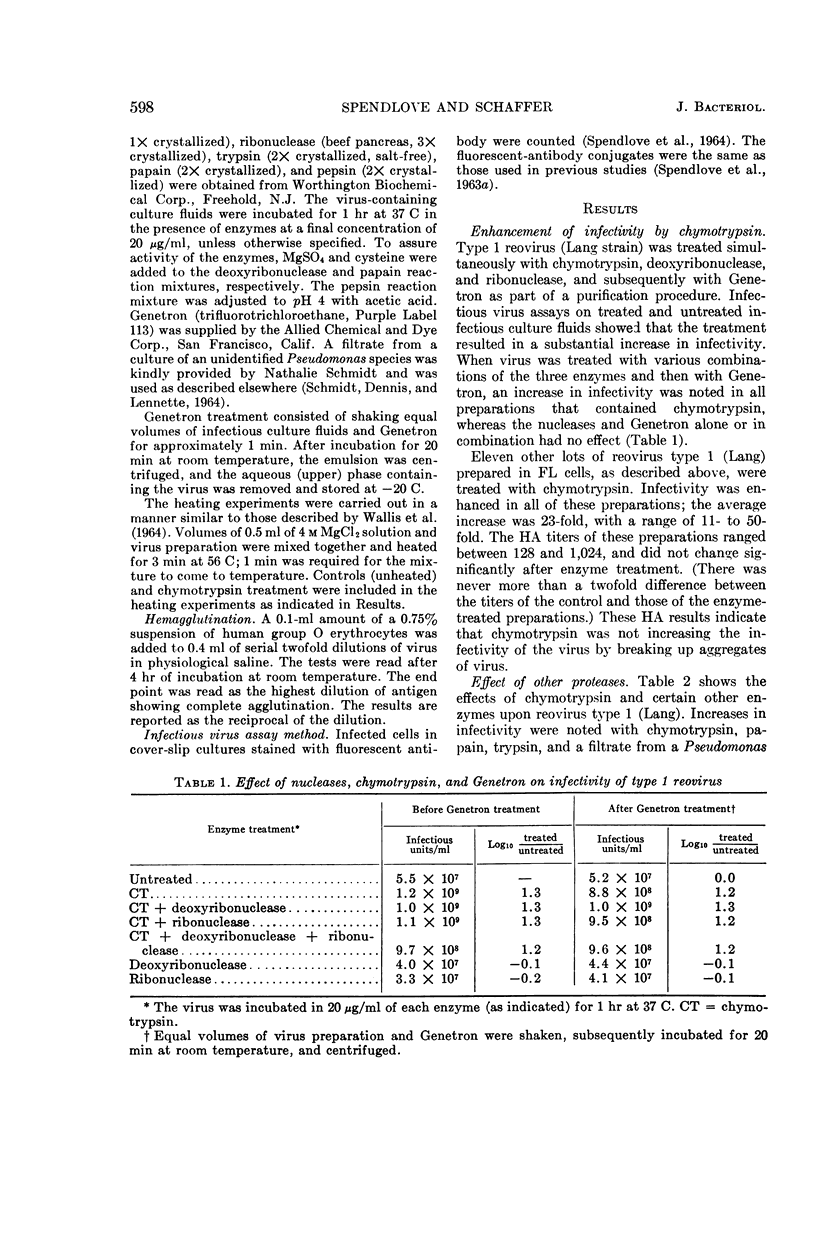
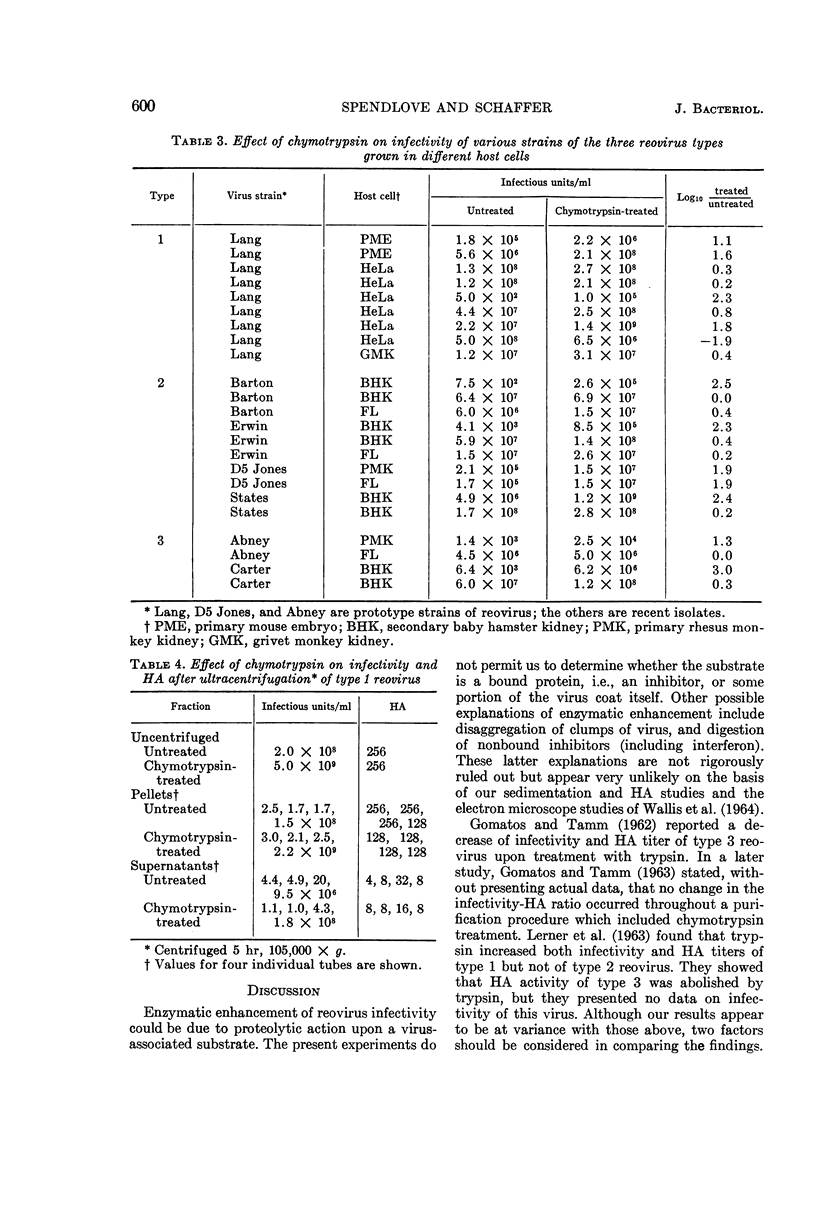
Spendlove, R. S. (California State Department of Public Health, Berkeley), and F. L. Schaffer. Enzymatic enhancement of infectivity of reovirus. J. Bacteriol. 89:597–602. 1965.—Enhancement of infectivity by chymotrypsin treatment has been demonstrated with all three types of reovirus, although not in all viral preparations. Enzyme treatment did not produce a simultaneous increase in the hemagglutinating activity of reovirus type 1 (the only type tested). The infectivity of reovirus type 1 (Lang strain) was increased by treatment with chymotrypsin, trypsin, papain, and a filtrate from a culture of a Pseudomonas sp. but not by treatment with pepsin. Sedimentation experiments showed that the property of enhanceability was closely associated with the virus particles themselves. Results of studies involving various sequential treatments with chymotrypsin, and with heat in the presence or absence of 2 m MgCl2, were compatible with the interpretation that inhibited virus is resistant to exposure to a temperature of 56 C in the absence of MgCl2, whereas activated virus is thermolabile. Activation of reovirus infectivity by heat in the presence of MgCl2 and by chymotrypsin was not additive.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BELL T. M., MASSIE A., ROSS M. G., WILLIAMS M. C. ISOLATION OF A REOVIRUS FROM A CASE OF BURKITT'S LYMPHOMA. Br Med J. 1964 May 9;1(5392):1212–1213. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5392.1212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDFIELD M., SRIHONGSE S., FOX J. P. Hemagglutinins associated with certain human enteric viruses. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957 Dec;96(3):788–791. doi: 10.3181/00379727-96-23609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOMATOS P. J., TAMM I. Reactive sites of reovirus type 3 and their interaction with receptor substances. Virology. 1962 Jul;17:455–461. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90140-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomatos P. J., Tamm I. THE SECONDARY STRUCTURE OF REOVIRUS RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 May;49(5):707–714. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.5.707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HSIUNG G. D., MELNICK J. L. Morphologic characteristics of plaques produced on monkey kidney monolayer cultures by enteric viruses (poliomyelitis, Coxsackie, and echo groups. J Immunol. 1957 Feb;78(2):128–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEINSCHMIDT A. K., DUNNEBACKE T. H., SPENDLOVE R. S., SCHAFFER F. L., WHITCOMB R. F. ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF RNA FROM REOVIRUS AND WOUND TUMOR VIRUS. J Mol Biol. 1964 Nov;10:282–288. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80046-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANGRIDGE R., GOMATOS P. J. The structure of RNA. Reovirus RNA and transfer RNA have similar three-dimensional structures, which differ from DNA. Science. 1963 Aug 23;141(3582):694–698. doi: 10.1126/science.141.3582.694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LERNER A. M., CHERRY J. D., FINLAND M. Hemagglutination with reoviruses. Virology. 1963 Jan;19:58–65. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90024-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAISEL J., MOSCOVICI C. Plaque formation with ECHO virus types 15 to 24. J Immunol. 1961 Jun;86:635–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMIDT N. J., DENNIS J., LENNETTE E. H. STUDIES ON FILTRATES FROM CULTURES OF A PSYCHROPHILIC PSEUDOMONAS SP. WHICH INACTIVATE NONSPECIFIC SERUM INHIBITORS FOR CERTAIN HEMAGGLUTINATING VIRUSES. J Immunol. 1964 Jul;93:140–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPENDLOVE R. S., LENNETTE E. H., CHIN J. N., KNIGHT C. O. EFFECT OF ANTIMITOTIC AGENTS ON INTRACELLULAR REOVIRUS ANTIGEN. Cancer Res. 1964 Nov;24:1826–1833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPENDLOVE R. S., LENNETTE E. H., JOHN A. C. THE ROLE OF THE MITOTIC APPARATUS IN THE INTRACELLULAR LOCATION OF REOVIRUS ANTIGEN. J Immunol. 1963 Apr;90:554–560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPENDLOVE R. S., LENNETTE E. H., KNIGHT C. O., CHIN J. N. DEVELOPMENT OF VIRAL ANTIGEN AND INFECTIOUS VIRUS IN HELA CELLS INFECTED WITH REOVIRUS. J Immunol. 1963 Apr;90:548–553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALLIS C., MENICK J. L. Cationic stabilization--a new property of enteroviruses. Virology. 1962 Apr;16:504–506. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90234-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALLIS C., SMITH K. O., MELNICH J. L. REOVIRUS ACTIVATION BY HEATING AND INACTIVATION BY COOLING IN MGC12 SOLUTIONS. Virology. 1964 Apr;22:608–619. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90083-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


