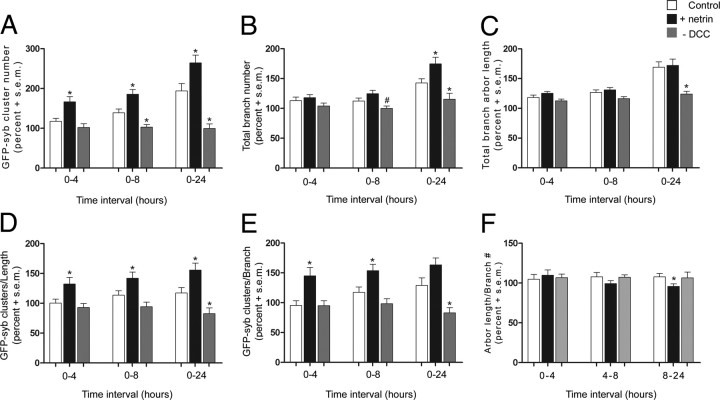
Figure 4.
DCC-mediated netrin signaling contributes to RGC axon presynaptic differentiation during the development of retinotectal connectivity. Changes in RGC presynaptic differentiation and in axon arborization were measured and expressed as percentage of initial values for each individual axon. A, Microinjection of recombinant netrin-1 into the optic tectum induced a significant increase in GFP-synaptobrevin-labeled presynaptic sites when compared with controls over a 24 h observation period. In contrast, microinjection of DCC function-blocking antibodies prevented the normal increase in presynaptic site number observed in controls over the 24 h observation period. B, Even though netrin induces a significant net increase in branches 8 h after treatment (Fig. 3C), the increase in branch number in RGC axons in netrin-treated tadpoles relative to the initial branch number was significantly different from controls by 24 h only. In contrast, anti-DCC treatment prevented the increase in branch number observed in controls at 8 and 24 h. C, The effect of anti-DCC treatment on axon arbor growth is also demonstrated by measuring the change in total arbor branch length. Total arbor branch length in RGC axons increased by 24 h in both control and netrin-treated tadpoles, whereas this measure was unchanged in the anti-DCC-treated tadpoles. D, E, The number of GFP-synaptobrevin-labeled presynaptic sites per unit arbor length and per branch number provided a measure of presynaptic site density. Netrin treatment significantly increased presynaptic site density in RGC axons from 4 h onward, whereas anti-DCC treatment resulted in RGC axons with lower presynaptic site density relative to controls by 24 h. F, We obtained a comparative measure of branch length by calculating average axon segment length (length/branch) at each observation interval and expressing it as percentage of initial value for each axon. This measure revealed that, on average, axon branch segments in RGC axon arbors in netrin-treated tadpoles became shorter than controls from 8 to 24 h after treatment. *Significance with p ≤ 0.05. #Trend toward significance with 0.05 > p < 0.10. Error bars indicate SEM.