Figure 6.
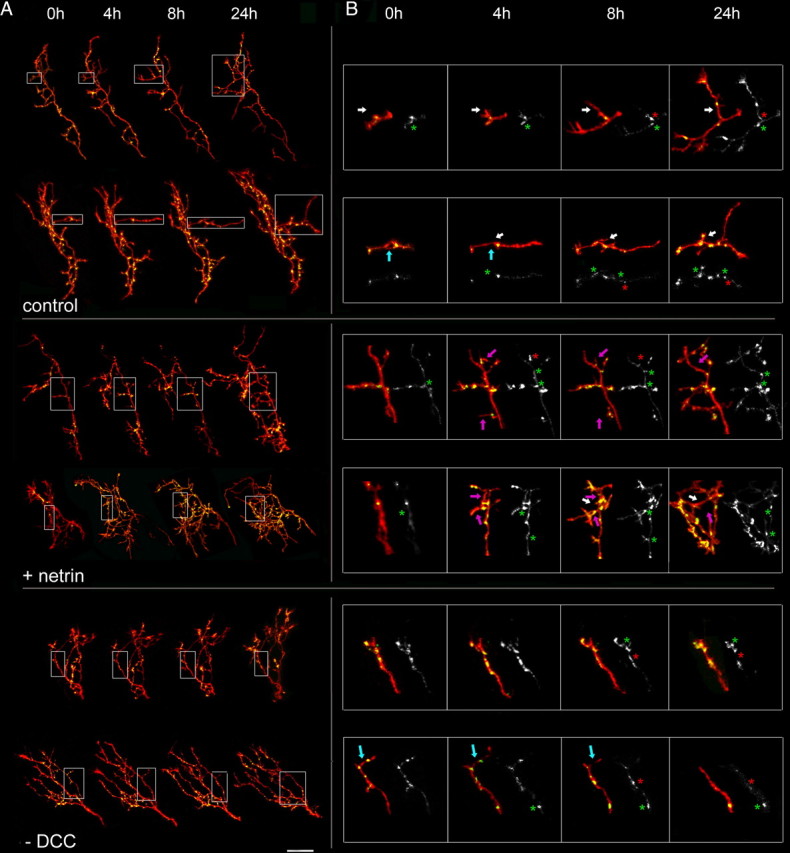
Dynamic changes in presynaptic structure in RGC axon arbors in response to alterations in netrin signaling. A, Confocal projections of representative RGC axons coexpressing Ds-Red (red) and GFP-synaptobrevin (green) in tadpoles microinjected with netrin-1 (+ netrin) or DCC function-blocking antibodies (− DCC) right after the first imaging session. Note the significantly higher number of GFP-synaptobrevin-labeled presynaptic sites in the morphologically more complex arbors after netrin treatment. In contrast, the RGC axon arbors that received anti-DCC treatment did not change their morphology or presynaptic connectivity significantly within a 24 h period (Fig. 7). Scale bar, 50 μm. B, Enlarged projections of single branches for the sample control-, netrin-, and anti-DCC-treated axons shown in A (gray boxes) illustrate branch and presynaptic site dynamics. Sample branches that were added (white arrows), eliminated (blue arrows), or added and then eliminated (magenta arrows) are shown for each experimental group. More branches were added and then eliminated (magenta arrows) in RGC arbors of netrin-treated tadpoles compared with controls. Although fewer in number, newly added branches in controls tended to remain stable for the remainder of the observation period (white arrows). Preexisting branches were eliminated (blue arrows) after anti-DCC treatment, whereas no new branches were added during the 24 h observation period. Sample GFP-synaptobrevin puncta added (green asterisks) or eliminated (red asterisks) highlight presynaptic site dynamics in the individual axon branches. Note that more GFP-synaptobrevin puncta were added per axon branch within the first 4 h after netrin treatment, and then the number continued to increase more gradually during the remainder of the 24 h observation period. Here, the green asterisks highlight a few examples. In comparison, axon branches in control-treated tadpoles underwent a slower increase in the number of GFP-synaptobrevin puncta across time points, whereas axons added fewer GFP-synaptobrevin puncta after anti-DCC treatment relative to controls. The relative rate of disassembly of GFP-synaptobrevin puncta (red asterisks) in axon branches was similar to controls for both netrin and anti-DCC-treated tadpoles.
