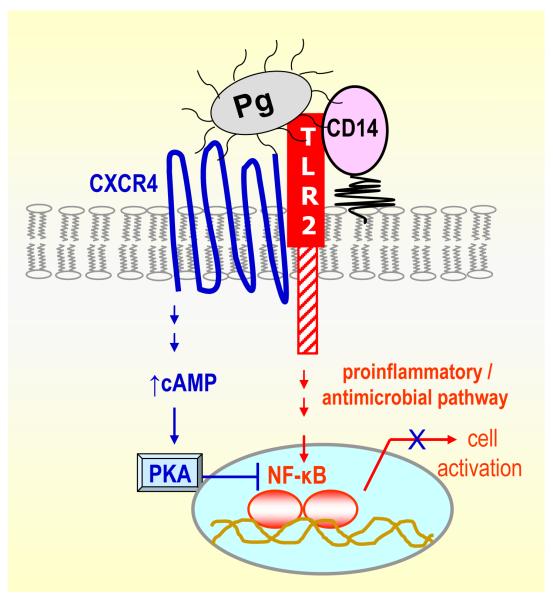
Fig. 2. Inhibition of TLR2-mediated innate immune responses through P. gingivalis exploitation of CXCR4.
P. gingivalis instigates a molecular cross-talk between CXCR4 and TLR2 in macrophage lipid rafts. Unlike CD14 which facilitates TLR2 activation by P. gingivalis (86), CXCR4 suppresses TLR2 signalling (89). Specifically, the pathogen binds CXCR4 and induces cAMP-dependent PKA signalling, which in turn inhibits TLR2-mediated nuclear factor-κB activation. This promotes the in vivo survival of the pathogen, unless CXCR4 is blocked by specific antagonists (89).