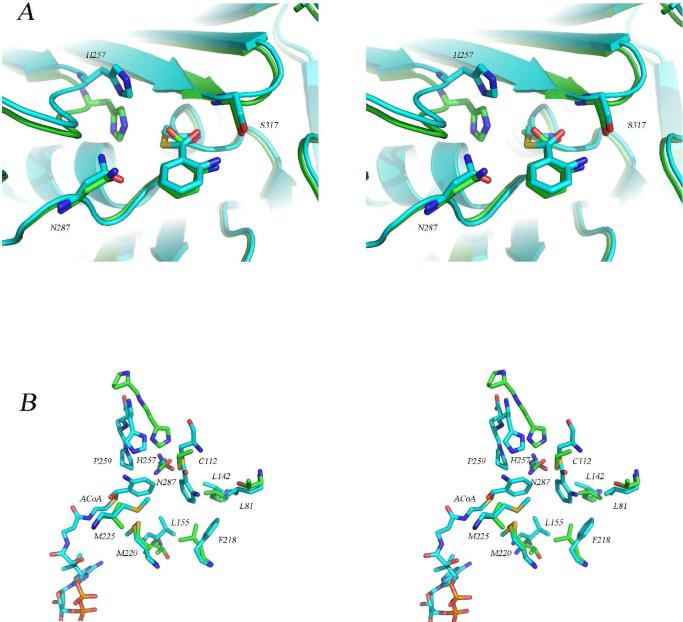
Figure 5.
Comparison of the structure of the PqsD covalent intermediate with the structures of the Cys112Ala mutant and with E. coli FabH. (A) Stereoview of the superimposed active sites of the covalent PqsD-anthranilate complex (blue) and the Cys112Ala mutant structure in complex with anthranilate (green) illustrating the similarity in the positions of the anthraniloyl rings and the differences in the positions of His257. (B) Stereoview of the superimposed active sites of the covalent PqsD-anthranilate complex (blue) and FabH from E. coli (green) illustrating the differences in the position of the active site histidine residue and the possible role of an active site proline. In FabH, His244 is preceded by Pro243 while in PqsD, His257 is followed by Gln258 and Pro259. Also shown is the ACoA molecule occupying the active site entry tunnel and the hydrophobic pocket surrounding the reaction intermediate.