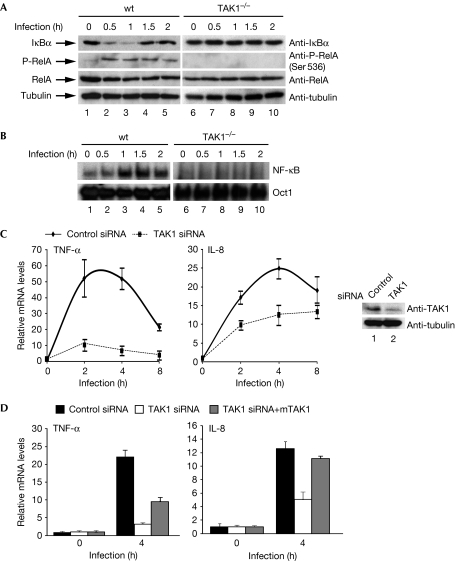
Figure 2.
TAK1 is required for Helicobacter pylori-induced NF-κB activation. (A) Levels of IκBα, phosphorylated Ser 536 RelA, RelA, TAK1 and tubulin were detected in the lysates from wt or TAK1−/− MEFs infected with H. pylori. (B) EMSA was performed using whole-cell extracts from wt or TAK1−/− MEFs infected with H. pylori, as in Fig 1B. (C) AGS cells transfected with control or TAK1 siRNA were infected with H. pylori and RT–PCR was performed to analyse NF-κB target gene expression. Levels of TAK1 and tubulin are shown in the right panels. (D) AGS cells transfected with control siRNA or TAK1 siRNA were reconstituted with mouse TAK1 (mTAK1), followed by infection for 4 h with H. pylori. Gene expression was analysed as shown in (C). EMSA, electrophoretic mobility-shift assay; IL-8, interleukin-8; MEF, mouse embryonic fibroblast; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; RT–PCR, real-time PCR; siRNA, short interfering RNA; TAK1, transforming growth factor-β-activated kinase 1; TNF-α, tumour necrosis factor-α; wt, wild type.