Figure 2.
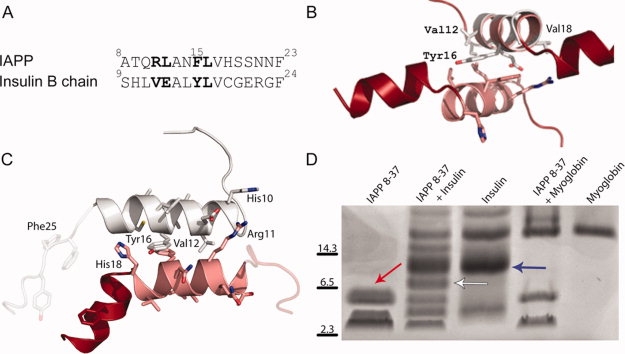
The homodimerization of IAPP suggests an analogous structure for IAPP-insulin heterodimerization. (A) Sequence alignment of residues 8–23 from IAPP with residues 9–24 of the insulin B chain. (B) The putative IAPP-interacting segment from insulin (helical segment composed of residues 9–20 shown in gray) is shown overlaid on the IAPP 8–19 helix. This interaction is centered on the stacked aromatic sidechains (Phe 15 from IAPP and Tyr 16 from insulin) between the two helices. (C) Computationally energy-minimized packing between insulin 9–19 and IAPP 8–18 helices. Notice that the energy-minimized helices are more parallel than the helices in B. (D) Crosslinking of IAPP and Insulin reveals an IAPP dimer (red arrow), an insulin dimer (blue arrow) as well as an IAPP-insulin heterodimer (white arrow). IAPP also crosslinks to higher-order insulin multimers. Myoglobin is included as a negative control for nonspecific crosslinking with IAPP.
