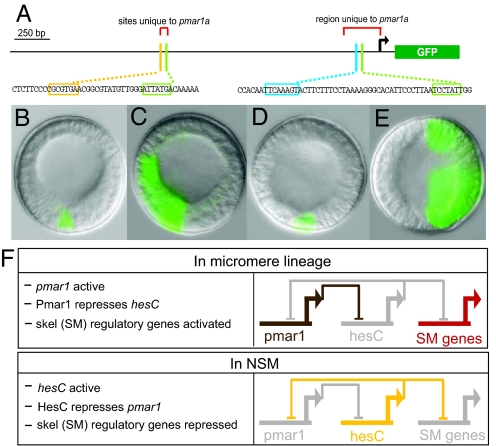
Fig. 1.
Exclusive regulatory domains established by reciprocal repression between pmar1 and hesC. (A) Diagram of a 2.59-kb fragment upstream of the pmar1a start of translation fused with the coding sequence for the GFP reporter. Small portions of the sequence are reproduced below to indicate highlighted transcription factor target sites discussed in the text. The bent arrow indicates the start of transcription. (cf. Fig. S1). (B–E) Typical results in embryos bearing pmar1a expression constructs at 16 h postfertilization: (B) wild-type pmar1 reporter activity (this construct expressed only in micromere descendants in 124 of 135 GFP+ embryos); (C) pmar1 construct but with HesC target site shown in A disrupted (result is gross ectopic activity in 77 of 92 embryos harboring construct). (D) Normal skeletogenic mesenchyme (SM) expression of wild-type pmar1 construct in presence of coinjected control morpholino antisense oligonucleotide (MASO). (E) Wild-type pmar1 construct in presence of coinjected HesC MASO resulted in ectopic expression in nearly all embryos (56 of 61). (F) Summary of regulatory interactions from refs. 1 and 8 and these experiments.