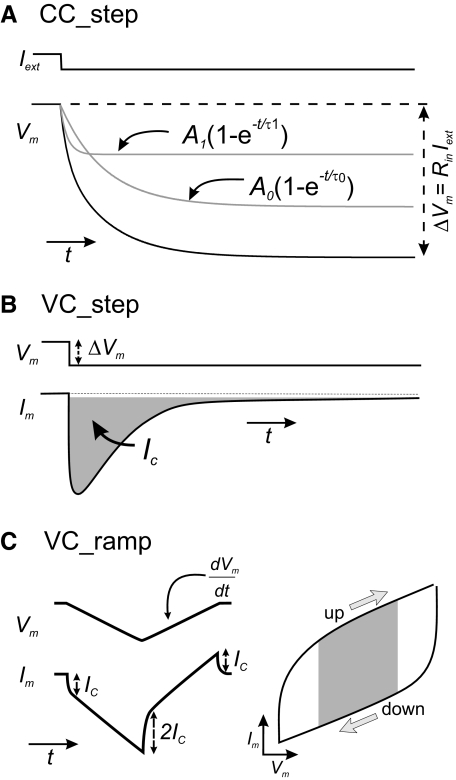
Fig. 1.
Total membrane capacitance measurement protocols. Schematic diagrams representing the protocols used. A: current-clamp step. The membrane potential change (black trace) elicited by a 1-s-long current step (Iext) was fitted with 2 exponentials (gray traces). The slowest component corresponds to the charging of the membrane capacitor. B: voltage-clamp step. The area under the capacitive current transient (gray) is the charge deposited on the membrane for a given ΔVm. The duration of this pulse is typically shorter than that of the current-clamp steps. C: voltage-clamp ramp. Membrane potential ramps elicit a capacitive current step Ic. The sign of Ic depends on the slope of the voltage ramp. If a symmetric voltage ramp is used, the difference between the values of Im measured at the same membrane potential during the up and down ramps is equal to 2Ic. This value was calculated by measuring the average current value of the upper and the lower branches over the grayed area in the current–voltage (I–V) curve and dividing by 2(dV/dt) (see methods; arrows correspond to the slope of the voltage ramp).