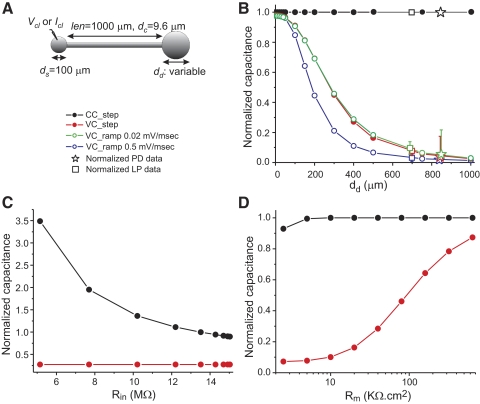
Fig. 3.
Effect of measurement protocol on total membrane capacitance estimates in a simple neuronal model. A: diagram of the model cell. The length of the neurite is 0.25λ. B: the capacitance in the model was determined with the three protocols described in methods and with two ramp slopes. Values were normalized against the actual total capacitance of the cell and are plotted against the diameter of the dendritic compartment. Normalized capacitance values measured in PD neurons (n = 29) and LP neurons (n = 19) using the same protocols as in the model. Capacitance values of each PD and LP neuron recorded were normalized to the neuron's own current-clamp–measured capacitance (Table 1). C: dependence of the measurements on soma and input resistance. The model cell shown in A with a dendrite diameter of 400 μm was used and the conductance of the soma compartment was varied (0.5 to 125 nS). The capacitance was measured with the CC_step and VC_step methods in response to 1-s-long current and voltage pulses, respectively, and normalized by the actual cell capacitance. The input resistance Rin was measured using Ohm's law. D: dependence of the measurements on specific membrane resistivity. The model cell shown in A with a dendrite diameter of 400 μm was used and current-clamp and voltage-clamp pulses of 1-s duration were used. As in B, measured capacitance values were normalized against the actual total capacitance of the cell and are plotted against the specific membrane resistivity Rm.