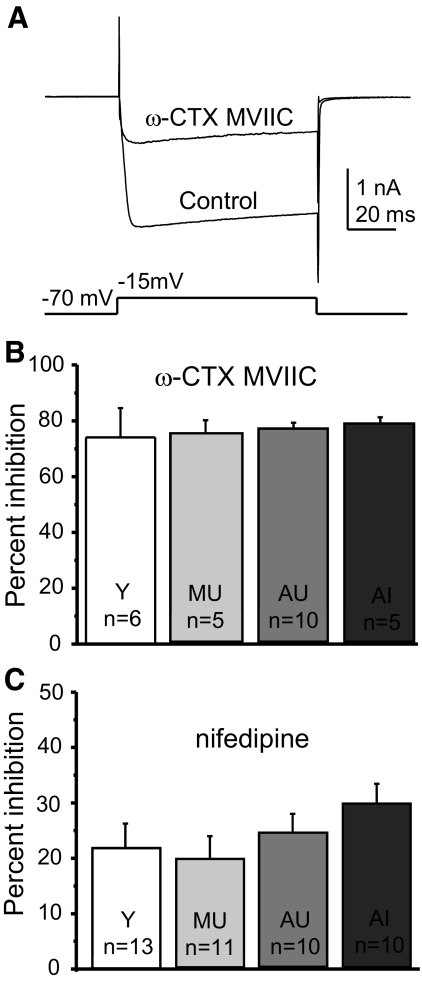
Fig. 3.
Perforated-patch recording of components of the HVA current in cholinergic BF neurons from behaviorally characterized rats. Ba2+ currents were generated in acutely dissociated voltage-clamped neurons by a voltage step from −70 mV to the peak current voltage determined by voltage ramp (as in Fig. 2). Control currents were compared with those in the presence of the HVA antagonists 10 μM nifedipine (blocks L-type current) and 500 nM ω-conotoxin (CTX) MVIIC (blocks N- and P/Q-type currents). A: example of calcium current block by CTX in a BF cholinergic neuron with peak HVA current occurring at −15 mV. The control HVA current is superimposed over the current in ω-CTX MVIIC. B: summary data show that there were no age- or cognition-related differences in the amount of HVA current block by ω-CTX MVIIC. C: summary data for inhibition by nifedipine. There were no significant differences in the amount of block by nifedipine. “n” values refer to the number of cholinergic neurons in the sample. Error bars represent SE.