Figure 9.
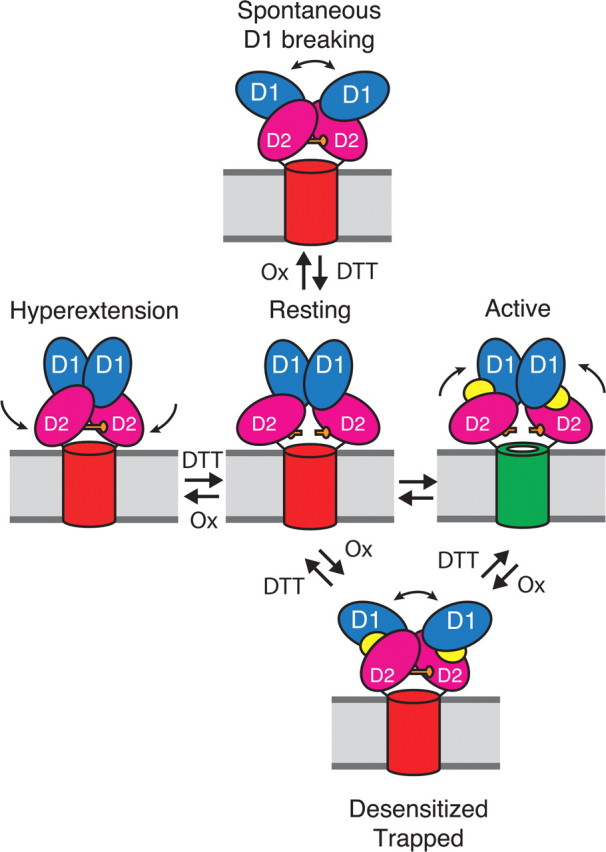
Diagram showing pathways for formation of D2 cross-links in AMPA receptors. One dimer of the two dimers in the receptor complex is depicted, with a cylinder representing the membrane-associated ion channel domain. The extracellular ligand binding clamshell domains have two lobes (D1, blue and D2, magenta). At rest, the ion channel is closed (red cylinder). The closure of the clamshell following the binding of glutamate (yellow) opens the channel (green); subsequent desensitization leads to disulfide bond cross-linking of the lower lobes (D2) between the introduced cysteine residues (orange bars). From the resting state two further conformational changes also lead to spontaneous D2 cross-linking. The first is dissociation of the active D1 dimer interface (top). The second is spontaneous hyperextension of the lower lobe of the ligand binding domain (left).
