Figure 7. Basis for the selectivity of OMTS recognition.
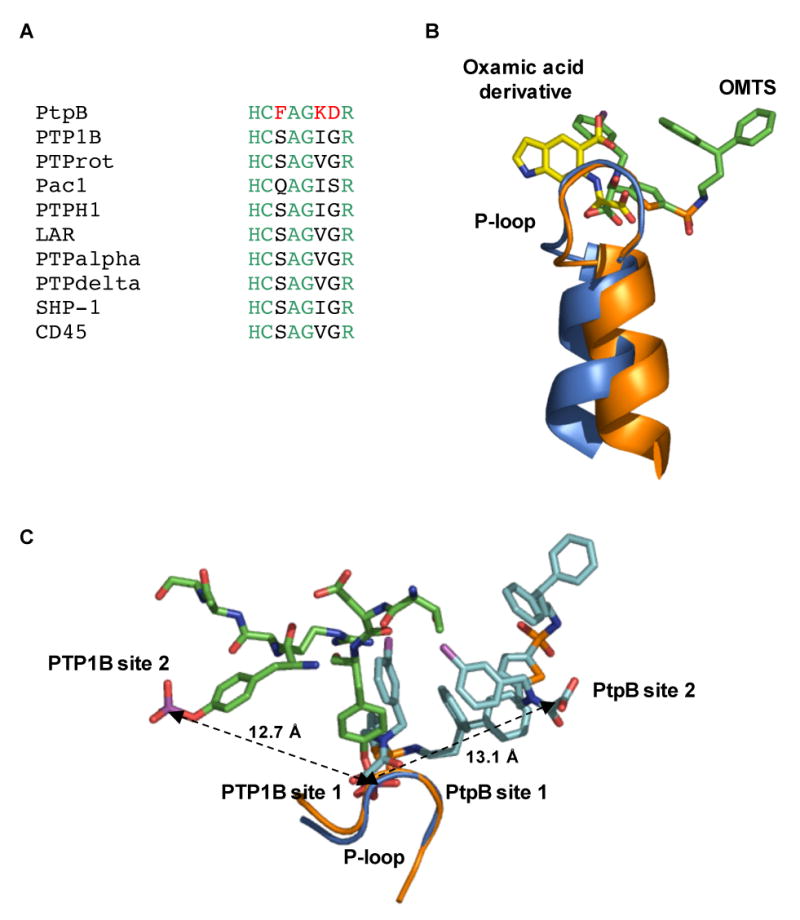
(A) Three (red) of the seven residues in the P-loop that make contacts to OMTS (Cys160-Arg166) are unique in PtpB compared to a variety of human conventional PTPs.
(B) Binding of the proximal OMTS (green) in the PtpB active site (blue) shows an alternative orientation of the oxalylamino group compared to the binding of a 2-(oxalylamino)-benzoic acid derivative (yellow) to PTP1B (PDB ID 1C88).
(C) Comparison of the phosphotyrosine binding sites of PTP1B (PDB ID 1G1H) and the two OMTS binding sites in PtpB. The second binding sites are positioned in opposite directions from the catalytic Cys in the two PTPs. A similar distance of ∼13 Å separates the adjacent pTyr phosphates bound to PTP1B and the oxamic acid groups of the proximal (site 1) and distal (site 2) OMTS molecules bound to PtpB.
