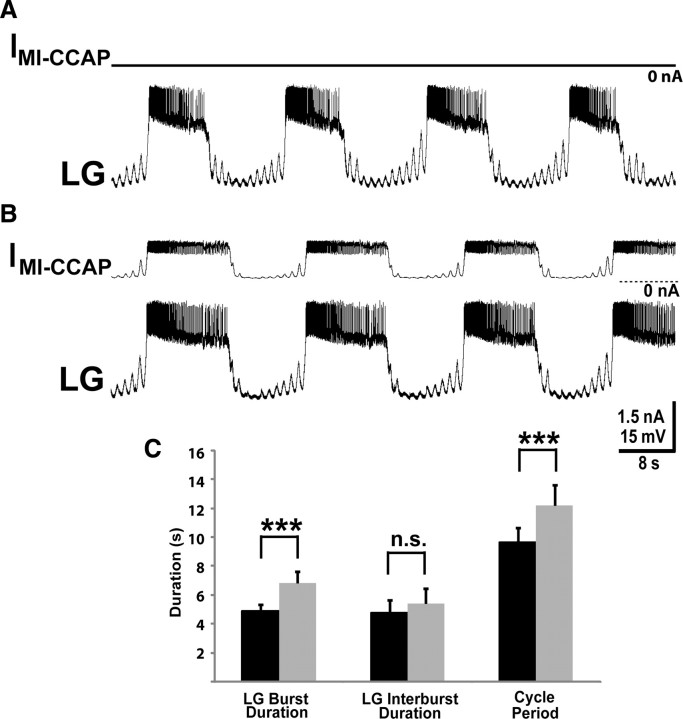
Figure 5.
Injection of an artificial IMI-CCAP into LG mimics the influence of bath-applied CCAP on the biological MCN1-gastric mill rhythm. A, A control gastric mill rhythm, represented by an intracellular LG recording, driven by tonic MCN1 stimulation (15 Hz) with no dynamic-clamp-mediated IMI-CCAP injected into LG. Most hyperpolarized Vm: LG, −65 mV. B, In the same LG recording as A, injection of an artificial IMI-CCAP into LG with the dynamic clamp selectively prolonged the gastric mill protraction phase. MCN1 stimulation was the same as in A. Note the relatively constant amplitude of the artificial IMI-CCAP during each LG burst. Most hyperpolarized Vm: LG, −66 mV. C, Dynamic-clamp-mediated injection of artificial IMI-CCAP into LG consistently prolonged the LG burst without altering the retraction duration, and thereby increased the gastric mill cycle period. Data are from 10 preparations. Black bars, MCN1 stimulation only; gray bars, MCN1 plus artificial IMI-CCAP; ***p < 0.005; n.s., not significant.