Figure 4. Vps4 binding sites on Vta1CTD.
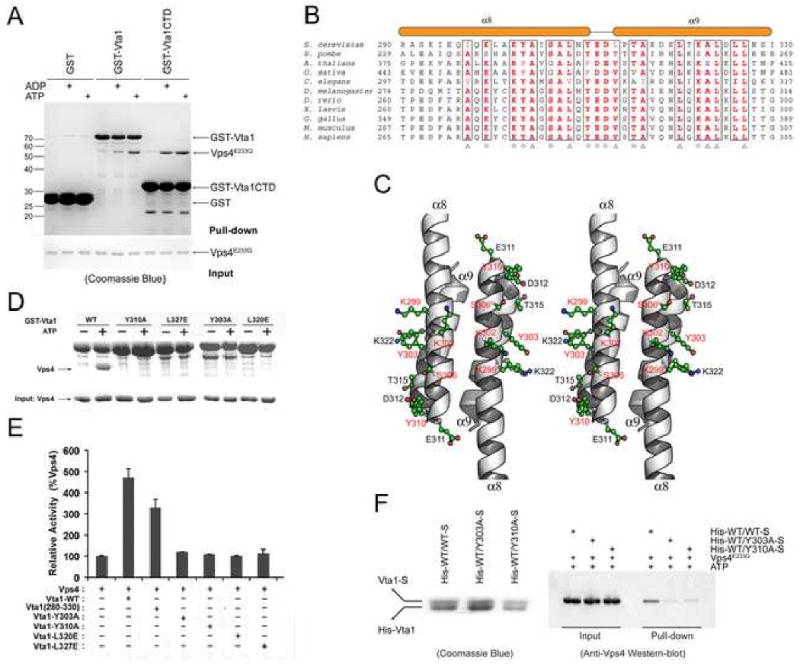
(A) In vitro analysis of Vta1-Vps4 interaction. Glutathione agarose beads pre-loaded with GST, GST-Vta1 or GST-Vta1CTD were incubated with purified Vps4E233Q under indicated conditions. Proteins retained on the beads were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and visualized by Coomassie blue staining. (B) Sequence alignment of Vta1CTD. Triangles indicate conserved residues involved in the dimer formation. Stars indicate conserved surface residues. Secondary structure elements are shown above the sequences. (C) Stereo view of the conserved surface residues on Vta1CTD. The residues demonstrated to be important for Vps4 interaction are highlighted in red. (D) Interactions between Vps4 and mutant Vta1 proteins. Purified Vps4E233Q were incubated with GST-tagged wild-type or point mutant Vta1 proteins in the presence of 2 mM ATP. Materials bound to glutathione agarose beads were analyzed by SDS PAGE and visualized by Coomassie blue staining. (E) ATPase activity of Vps4 in the presence of Vta1 proteins. The activity was normalized to Vps4 alone to compare the stimulation effects of different Vta1 proteins (error bars represent standard deviation of results from three independent measurements). (F) Interactions between Vps4 and Vta1 heterodimers. Vta1 heterodimers were co-expressed in pETDuet-1 vector such that the N-terminal His-tagged wild-type protein is in the first expression cassette and the C-terminal S-tagged wild-type or mutant protein is in the second expression cassette. Heterodimer proteins were isolated by tandem purification with Ni++-NTA resin and S-protein resin (left panel). Heterodimers retained on the S-protein resin were then used to pull down Vps4E233Q in the presence of 2mM ATP. Bound Vps4 proteins were analyzed on SDS-PAGE and detected by Western blotting with anti-Vps4 antibody (right panel). Figure 4C is prepared with Pymol (DeLano Scientific LLC).
