Fig. 5.
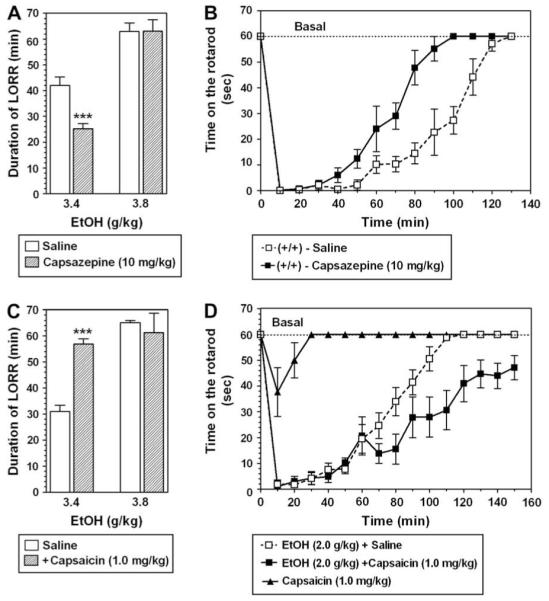
Capsazepine (10 mg/kg) and capsaicin (1.0 mg/kg) have opposite effects on ethanol-induced sedation and tolerance in wild type mice. A. Capsazepine significantly decreased the sedative effects of 3.4 g/kg ethanol but had no effect on a higher dose of ethanol in wild type mice (n = 7 for each group, ***p < 0.01 significant difference between saline and capsazepine for same dose of ethanol, Student t-test). B. Capsazepine decreased the recovery time for the motor impairing effect of ethanol (2 g/kg) in wild type mice (n = 6 for each group). C. Capsaicin significantly increased the sedative effects of the lower dose of ethanol (n = 6 for each group). D. Capsaicin increased the recovery time of the motor impairing effect of (EtOH) ethanol (2 g/kg) (n = 6-9 for each group, ***p < 0.001 significant difference between saline and capsaicin for same dose of ethanol, Student t-test). Values are mean ± SEM.
