Fig. 6.
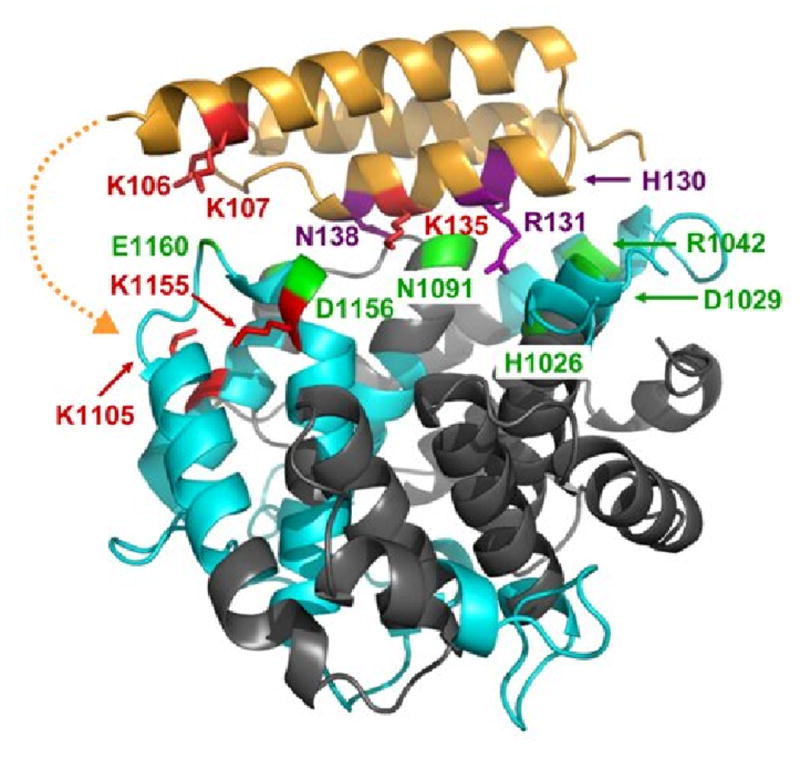
Interaction sites of C3d binding to Efb(-C) as determined by differential lysine acetylation. Efb-C is drawn as in Fig. 6, while C3d is shown in ribbons colored according to regions of peptide coverage as described in Table 2 (blue ribbon) and uncovered regions (slate). Selected contacting residues of C3d which bind to Efb-C according to x-ray crystallography are shown in green. These are H1026, D1029, R1042, N1091, S1097, D1156 and E1160. K1155 in fragment ISLQEAKDICEEQ VNSLPGSITKAGDFL (1149-1176) was protected in Efb-C/C3d, implying that D1156 may contact Efb-C. In addition, K1105 in fragment CGAVKW (1101-1106) was protected from acetylation in the complex. This suggested that portions of Efb(-C) not present in the crystal structure model may also be contacting C3d near residue K1105. The potential location for additional contacts invisible in the Efb-C/C3d crystal structure is depicted by a dashed orange line. No evidence was obtained regarding the role of R1042 in the Efb-C/C3d complex, since K1041 in fragment GLEKRQGAL (1038-1046) was solvent accessible in the complex. Similarly, no further information was available for H1026, D1029 and N1091, as no identified peptides covered this sequence, nor were there any lysine residues in these regions.
