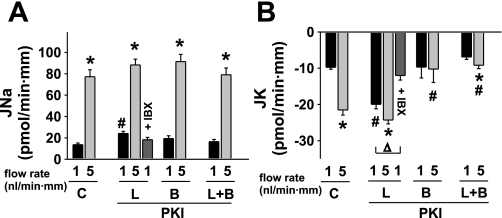
Fig. 1.
Effect of luminal (L) and/or basolateral (B) mPKI (5 μM) on basal and flow-stimulated net cation transport in isolated perfused rabbit cortical collecting ducts (CCDs). A: net Na absorption (JNa) increased in untreated control (C) tubules as the luminal flow rate was increased from 1 to 5 nl·min−1·mm−1. mPKI added to the luminal and/or basolateral solutions had no effect on flow-stimulated JNa, although the luminal inhibitor modestly increased JNa in tubules perfused at a slow flow rate. Luminal iberiotoxin (IBX), an inhibitor of BK but not ROMK channels, had no effect on baseline JNa in tubules perfused with mPKI. B: net K secretion (JK) increased ∼3-fold in response to a 5-fold increase in luminal flow rate in control CCDs. Addition of mPKI to the luminal but not basolateral solution increased JK in CCDs perfused at a flow rate of 1 nl·min−1·mm−1; a subsequent increase in flow rate augmented JK only slightly. Addition of mPKI to the basolateral solution alone or in the presence of luminal inhibitor inhibited flow stimulation of JK. Luminal IBX completely inhibited the mPKI-mediated increase in JK observed in CCDs perfused at a flow rate of 1 nl·min−1·mm−1. Values are means ± SE. For each protocol, n is indicated in results. *P < 0.05 compared with Jx at 1 nl·min−1·mm−1 in same tubules. #P < 0.05 compared with Jx in control tubules studied at same flow rate. Δ, P < 0.01 compared with JK at 1 nl·min−1·mm−1 in the same experimental group.