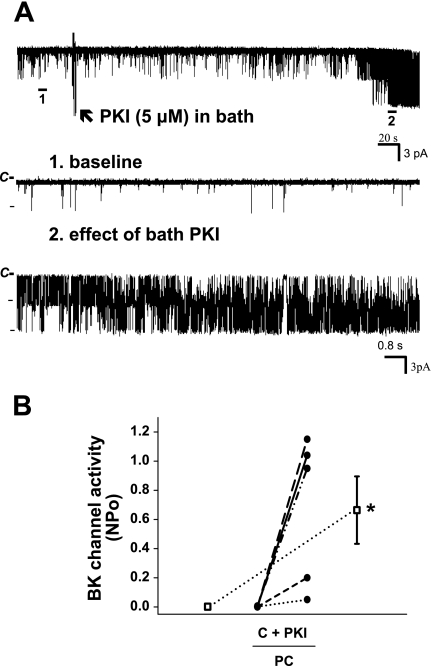
Fig. 4.
Effect of bath mPKI (5 μM) on BK channel activity in principal cells in the rat CCD. A: representative trace of the stimulatory effect of mPKI, added to the solution bathing a split-open CCD (arrow), on BK channel activity in a principal cell-attached patch studied at a holding potential of 0 mV. The top trace shows the time course of the entire experiment. Two parts of the trace are expanded (traces 1 and 2) to show detailed channel activity at faster time resolution. B: effect of mPKI, added to the solution bathing split-open CCDs, on NPo of the BK channel in individual cell-attached patches of PC (n = 5) studied at a holding potentials of 0 mV. PKI had no effect on BK channel activity in an additional 4 patches that did not respond to addition of ionomycin to the bath (which increases [Ca2+]i) with an increase in channel activity; this suggests that these nonresponsive cell-attached patches were devoid of BK channels. •, Paired data from individual cell-attached patches; □, means ± SE for the control and experimental data sets. *P < 0.05 compared with C.