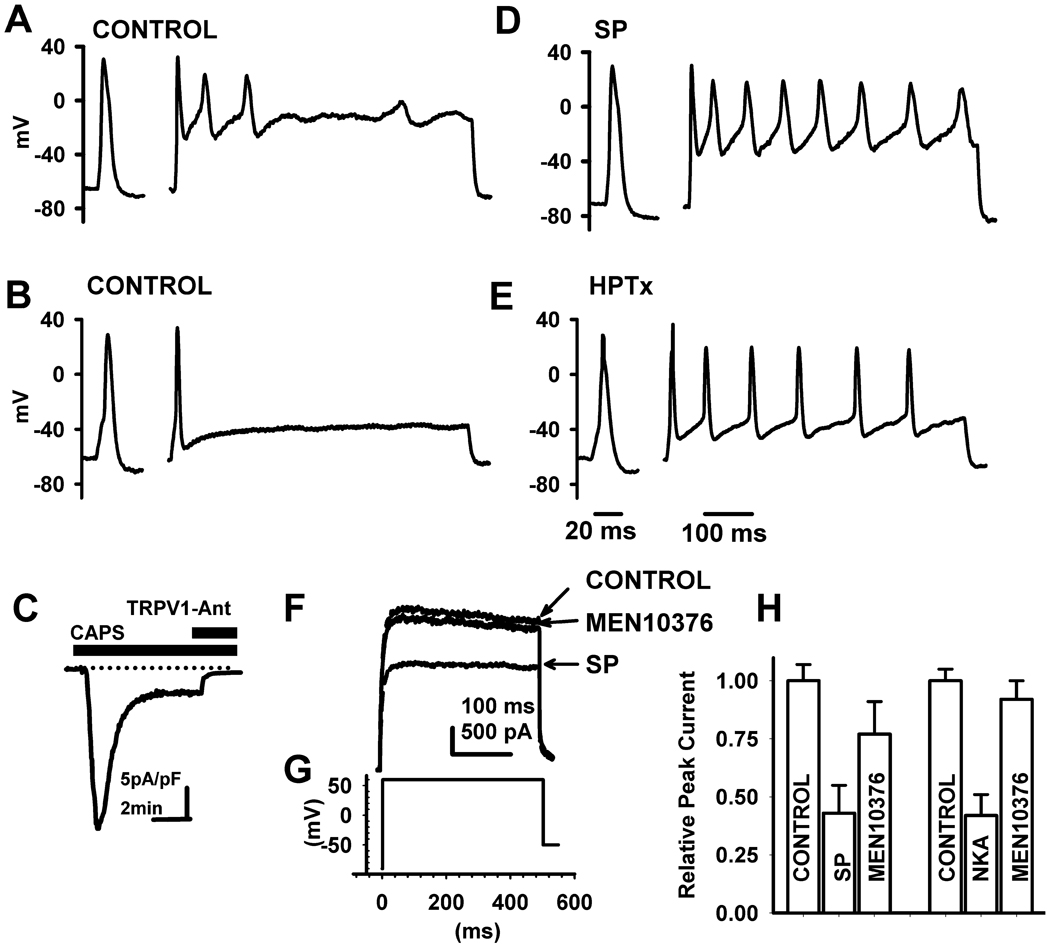
Fig. 1.
Effect of neurokinins on firing and K+ currents in capsaicin responsive (CR) DRG neurons. Action potentials generated in two different in CAPS-responsive (CR) phasic DRG neurons by rectangular current pulse injections 5 ms in duration and 200 pA (A, D) or 50 pA (B, E) in intensity, followed by a 100 ms interpulse at the holding potential and a second pulse of the same intensity as the first in the sequence, 600 ms in duration. Control recordings before treatment (A, B) and the enhancement of firing by substance P (SP, 0.5 µM, B) or by heteropodatoxin II (HPTx, 0.05 µM, E). SP (D) and HPTx (E) significantly increased the number of action potentials (APs) triggered by the second pulse in the sequence without significantly altering the duration of single AP triggered by the first brief pulse. C, Inward current evoked by CAPS (0.5 µM) is blocked by a TRPV1 antagonist (TRPV1-Ant, 5 µM). F, Total K+ currents activated by a test pulse to +60 mV from a holding potential of −80 mV were partially blocked by SP (0.5 µM) and the NK2 (0.5 µM) selective antagonist MEN10376 reversed the inhibitory effect of SP in the same cell shown in C. H, Summary of the effects of substance P or a selective NK2 agonist, [βAla8]-neurokinin A (4–10) (NKA, 0.5 µM) on total K+ currents in CR phasic DRG neurons and reversal of the effects by the NK2 (0.5 µM) selective antagonist MEN10376. Scale bar in A, B, D and E is 20 ms for the first action potential in the sequence and 100 ms for the second long stimulus pulse. Scale bars in F are 100 ms and 500 pA and in H are 5 pA/pF and 2 min.