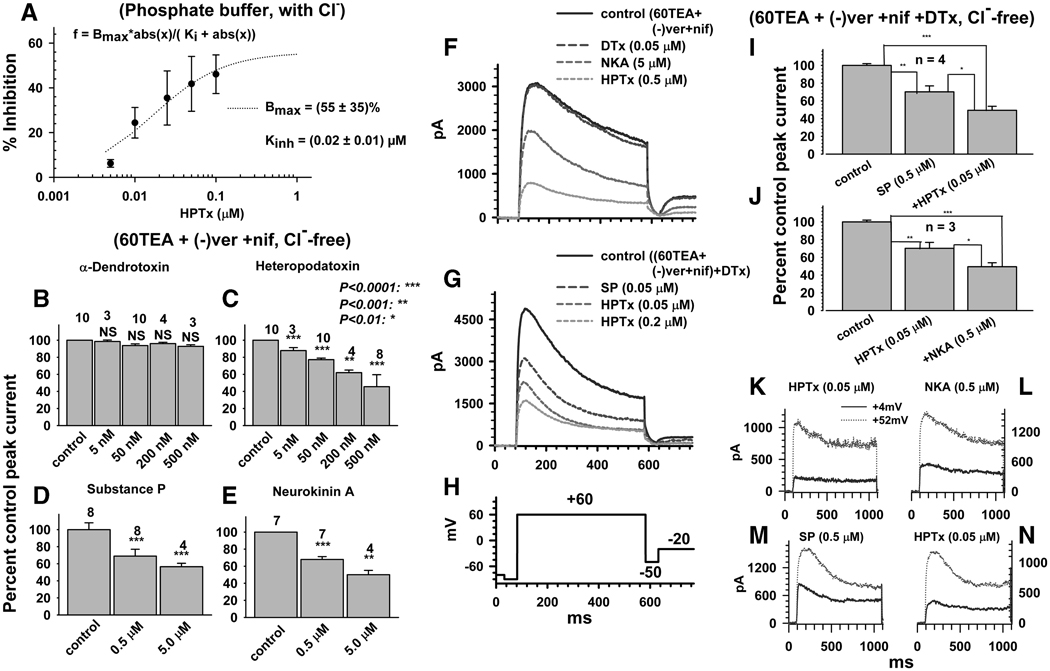
Fig. 6.
Effect of K+ blockers and neurokinins on pharmacologically isolated low threshold inactivating K+ currents. A, Concentration dependence of HPTx block of total K+ currents recorded in phosphate buffer saline and normal pipette solution. In all subsequent panels Cl− was substituted with methylsulfonate and 60 mM of extracellular Na+ was replaced with 60 mM TEA. B–E, Concentration dependence of the effects of DTx (B), HPTx (C), SP (D) and NKA (E) on K+ current recorded after addition of 5 µM (−) verapamil (ver) and nifedipine (nif). F, Effect of sequential addition of DTx, NKA and HPTx on TEA-verapamil-nifedipine insensitive inactivating K+ currents. G, Effect of sequential addition of SP (0.5 µM) and HPTx (0.05 and 0.2 µM) on DTx-TEA-verapamil-nifedipine insensitive inactivating K+ currents. H, Pulse protocol for the experiments in F and G. I, J, Cumulative block of DTx-, TEA-, verapamil-, nifedipine-insensitive inactivating K+ currents by sequential addition of SP and HPTx (I) or HPTx and NKA (J). K, L, Time course of currents inhibited by HPTx (K), NKA in the presence of HPTx (L), in the same neuron as in K. M, N, Time course of currents inhibited by SP (M) and HPTx in the presence of SP (N), in the same neuron as M. Currents obtained by subtraction of currents before and after addition of drugs and represent currents activated at either +4mV (smallest of the two traces) or +52 mV (largest of the two traces).