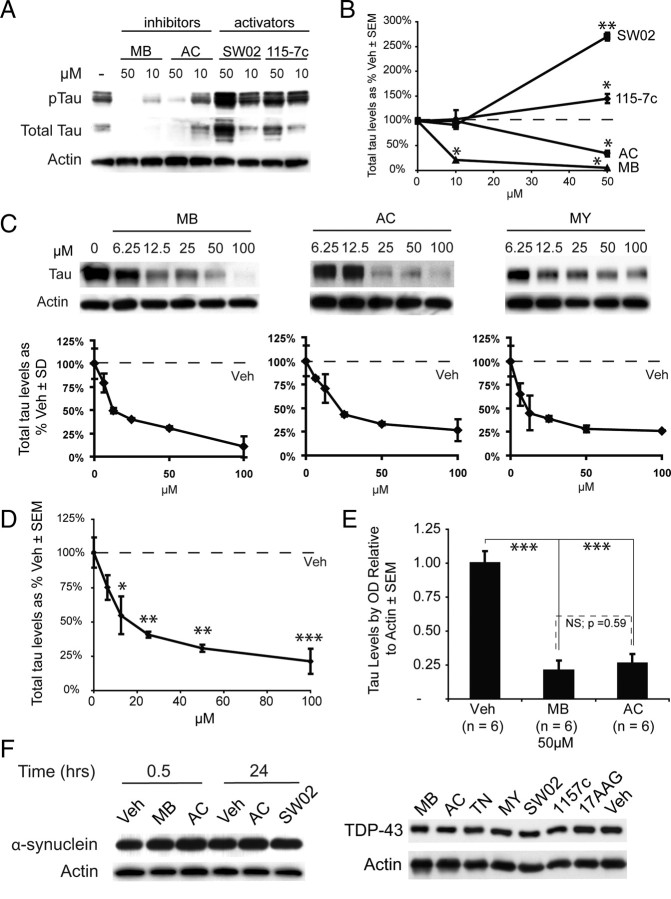
Figure 2.
Inhibitors of Hsp70 decrease tau levels, and activators protect them. A, HeLa tau transfectants were treated for 24 h with Hsp70 inhibitors (MB or AC) or activators (SW02 or 115-7c). B, Quantification plots of the Western blots after actin normalization illustrate significant decreases in total tau levels at higher doses of MB (▲) or AC (●), while treatment with either 115-7c (♦) or SW02 (■) increased tau levels. Analysis was performed using replicate blots. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. C, HeLa cells stably transfected with human 4R0N tau were treated with MB, AC, or MY for 3 h and harvested. Results are normalized to actin and compared with Veh. D, Combining all three inhibitors for more complete statistical analysis of Hsp70 inhibition demonstrated that significant reductions in tau levels were achieved at 12.5 μm, and significance increased with higher concentrations. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. E, Statistical analyses using multiple experiments (n = 6) across cell models demonstrate that MB and AC each significantly and consistently reduce tau levels at 50 μm. Moreover, MB and AC were not significantly different from each other. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. F, HeLa cells were transfected with either α-synuclein or TDP-43 and treated with indicated drugs [inhibitors in red, activators in blue, Hsp90 inhibitor (17AAG) and vehicle in black] for 30 min (α-synuclein) or 24 h (both α-synuclein and TDP-43). Levels of either protein were unaffected by any treatment under these conditions (for quantitation, see supplemental Fig. S1, available at www.jneurosci.org as supplemental material).