Figure 2.
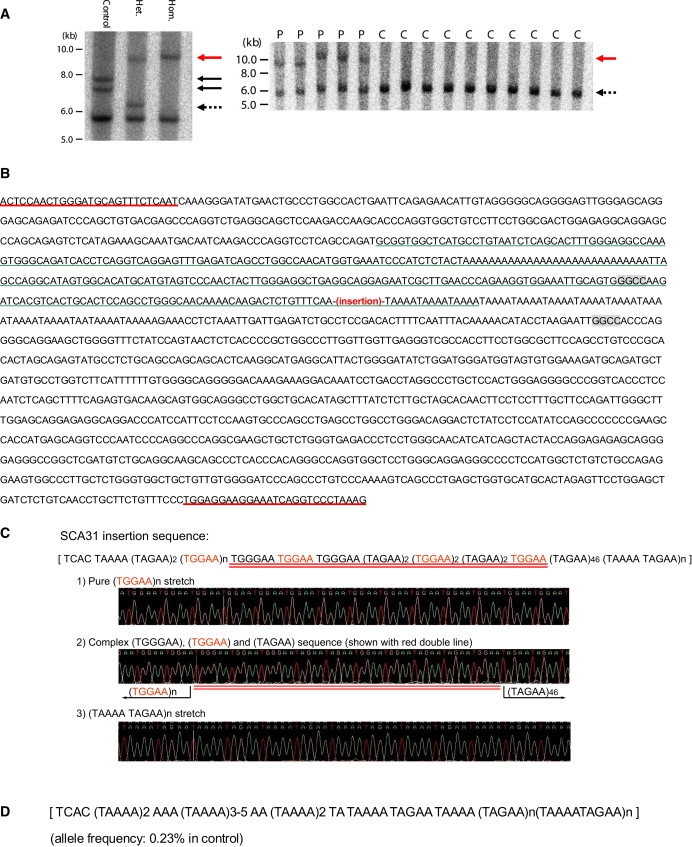
Identification of Complex Pentanucleotide Repeat Insertions in SCA31 Patients
(A) Southern blot analysis showing the SCA31 insertion. The left-hand panel shows EcoRI-digested genomic fragments detected with a cosmid probe for the region between nucleotides 65,083,571 and 65,124,051. A rare 1.5 kb insertion and an unusual 0.7 kb expanded (TAAAA)n (both shown with solid black arrows) were observed in one control (control 1). SCA31 insertions in two patients are shown with a red arrow. “Hom.” and “Het.” designate the homozygous patient and heterozygous patient, respectively. The dotted arrow indicates normal chromosomes without insertions. The thick 5.8 kb bands common in the three subjects show fragments outside the insertion site. The right-hand panel shows aberrant EcoRI-digested 9–10 kb genomic fragments (a red arrow) that completely segregated with SCA31 patients (P). All heterozygous patients (P) and controls (C) have “normal” 6 kb fragments (dotted arrows). Radiolabeled PCR products obtained by amplifying the 3009 bp genomic segment between nucleotides 65,079,127 and 65,082,135 on NCBI build 36.3 were used as probes.
(B) Sequences around the SCA31 insertion (chromosome16: nucleotides 65,081,260–65,082,786 on NCBI build 36.3). Flanking primers for PCR amplification (underlined in red) of insertion and flanking HaeIII recognition sites (in shaded boxes) are shown. The AluSx sequence30 is shown with a green underline. Without an insertion, PCR amplification with flanking primers and a subsequent HaeIII digestion will produce a DNA fragment 193 bp in length.
(C) The components of the SCA31 insertion in the homozygous patient. The SCA31 insertion consists of a preceding 4 bp TCAC and three different penta-nucleotides, (TGGAA)n, (TAGAA)n, and (TAAAA)n. (TGGAA)n is the patient-specific repeat (shown in red), and both (TGGAA)n and (TAAAATAGAA)n are pure stretches too long to be read through. The bridging sequence between (TGGAA)n and (TAGAA)46 is underlined in red.
(D) The sequence of the insertion in control 1. Rare insertions were observed in controls at the same position as the SCA31 insertion, but with shorter length and different components. The insertion in control 1 consisted of a preceding 4 bp TCAC and two pentanucleotide components, (TAGAA)n and (TAAAA)n. The (TGGAA)n was not detected.
