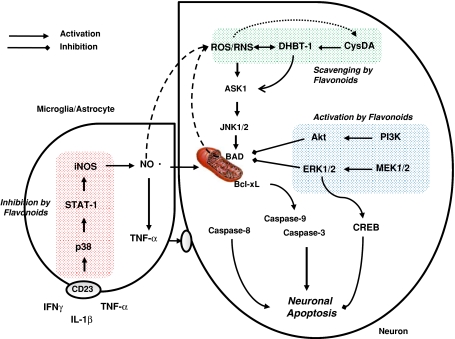
Fig. 2.
The cellular mechanisms by which flavonoids and their metabolites protect against neuroinflammation and neuronal injury induced by 5-S-Cys-DA, DHBT-1 and related ROS. Flavonoids inhibit the p38 pathway glia cells leading to a reduction in iNOS expression and NO• release. In neurons, they scavenge neurotoxic species and induce pro-survival signalling pathways, such as ERK1/2 and PI3-kinase/Akt, leading to an inhibition of neuronal apoptosis