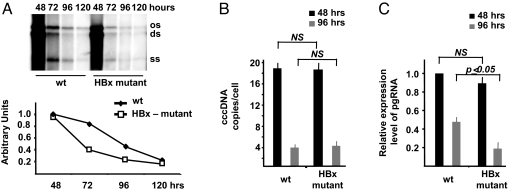
Fig. 1.
HBx is involved in viral replication, and it is required for HBV pregenomic RNA transcription. (A) HepG2 cells were transfected with monomeric linear full-length WT or HBx mutant HBV adw genomes, and cytoplasmatic HBV core particles were isolated at the indicated time points after transfection. (Upper) Southern blot analysis of HBV DNA replicative intermediates. (Lower) Densitometric quantification of HBV replicative intermediates. Signal intensity of the single-strand (SS) band underneath the linear double-stranded (DS) HBV DNA band was quantified with Quantity One 1-D Analysis Software (BioRad Laboratories). The band corresponding to the DS HBV DNA was not included in the quantitative analysis, because this DNA may be partially derived from transfected input DNA. The optical density value of the SS band at 48 h in WT replicating cells is set at 1.0. Data are expressed as relative arbitrary units (mean + SD) from three independent experiments. OC, open circular duplex HBV DNA; DS, double-strand; and SS, single-strand HBV DNA replicative intermediates. (B) cccDNA accumulation in HepG2 cells transfected with WT or HBx mutant HBV genomes. Real-time quantitative PCR analysis was performed using selective cccDNA primers to amplify cccDNA and beta-globin primers to normalize the DNA samples. Results are expressed as number of cccDNA copies per cell (mean + SD) from four independent experiments. (C) HepG2 were transfected with WT or with HBx mutant HBV genomes and mRNAs were extracted 48 and 96 h posttransfection as described in the Materials and Methods section. Specific primers were used to quantitate the HBV pregenomic RNA, and GAPDH amplification was used to normalize for equal loading of each RNA sample. Results are expressed as number of cccDNA copies per cell (mean + SD) from three independent experiments. pgRNA, HBV pregenomic RNA.