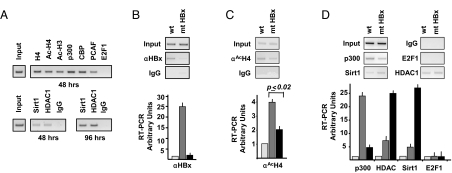
Fig. 3.
HBx modulates the epigenetic control of cccDNA function by affecting the recruitment of chromatin modifying enzymes. (A) HepG2 cells were transfected with monomeric linear full-length HBV DNA. (Upper) Chromatin prepared 48 h after transfection was immunoprecipitated with the relevant control IgG or specific anti-H4, anti-AcH3, anti-AcH4, anti-p300, anti-CBP, anti-PCAF, and anti-E2F1 antibodies and analyzed by PCR with HBV cccDNA selective primers. (Lower) Chromatin prepared 96 h posttransfection was immunoprecipitated with the relevant control IgG or specific antibodies to the class I HDAC1 and class III hSirt1 histone deacetylases. ChIPed DNA was analyzed by PCR with HBV cccDNA selective primers. (B–D) Chromatin was prepared from HepG2 cells transfected with WT or HBx mutant monomeric linear full-length genomes and immunoprecipitated with the relevant control IgG or a specific anti-HBx (B), anti-AcH4 (C), anti-p300, anti-HDAC1, anti-hSirt1, and anti-E2F1 (D) antibodies. Immunoprecipitated chromatin was analyzed by semiquantitative PCR (Upper) and real-time quantitative PCR (Lower) with HBV cccDNA selective primers. Light gray columns, mock; gray columns, WT HBV; black columns, mt HBx. Results are expressed as RT-PCR arbitrary units (mean + SD) from four independent experiments.