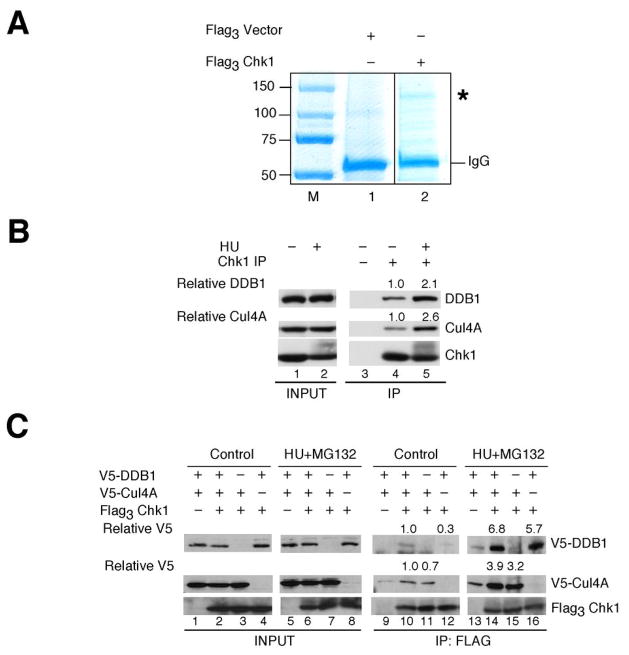
Figure 1.
Proteomic screen identifies DDB1 as a novel Chk1 interacting protein. A, lysates prepared from HU-treated HEK293 cells transfected with control plasmid or plasmid encoding Flag3Chk1 were incubated with Anti-Flag M2-Agarose. Washed precipitates were then incubated in lysates prepared from HU-treated HEK293 cells. Bound proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE and stained with Colloidal Coomassie Blue. The band denoted by an asterisk (*) was present in Flag3 Chk1 but not control precipitates. This protein was excised from the gel and identified as DDB1 by mass spectrometry. B, endogenous Chk1 was immunoprecipitated from control cells or cells treated with 20 mM HU for 6 h. Cells were also treated with 10 μM MG132 for 2 h prior to harvest. Precipitates were resolved by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by Western blotting. Densitometry was performed to determine relative amounts of DDB1 and Cul4A in Chk1 immunoprecipitates (n = 3). C, HeLa cells expressing the indicated tagged proteins were cultured in the presence of 20 mM HU and 50 μM MG132 for 4 h. Flag3Chk1 was immunoprecipitated and precipitates were analyzed by Western blotting. Densitometry was performed to quantitate relative amounts of DDB1 and Cul4A in Chk1 immunoprecipitates (n = 2). Relative levels of DDB1 and Cul4A are indicated.