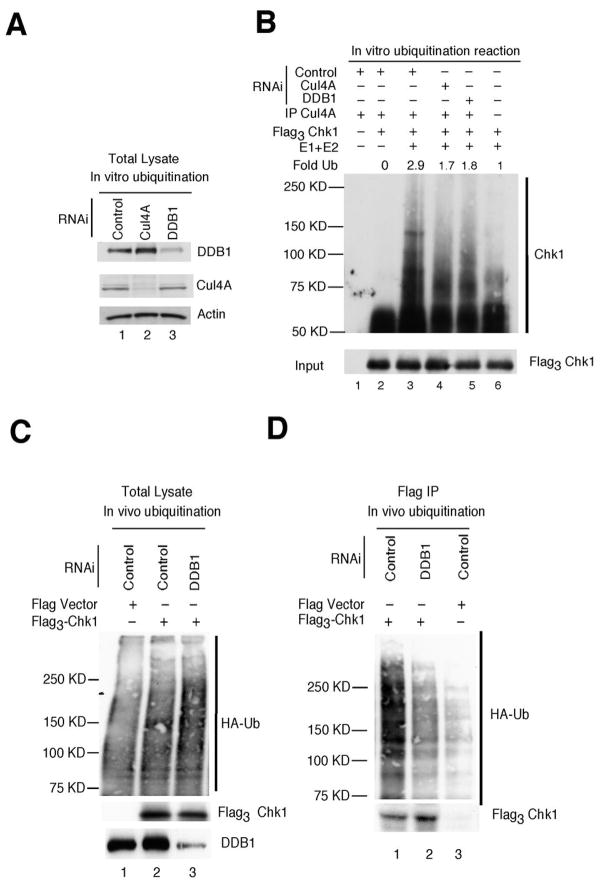
Figure 3.
Chk1 ubiquitination by Cul4A/DDB1. A, asynchronously growing HeLa cells transfected with RNAi targeting luciferase (control, lane 1), Cul4A (lane 2) or DDB1 (lane 3) were cultured in the presence of HU for 1h. Lysates were prepared and resolved directly by SDS-PAGE (A) or were incubated with a Cul4A-specific antibody to precipitate the Cul4A-containing E3 ligase for ubiquitination assays (B). B, Cul4A immunocomplexes were incubated alone (lane 1), with Flag3Chk1 precipitates (lane 2) or with Flag3Chk1 precipitates and purified E1 and E2 (lanes 3, 4, 5). Flag3Chk1 precipitates were also incubated with purified E1 and E2, in the absence of Cul4A immunocomplexes (lane 6). Ubiquitination assays were performed in vitro and reaction products were resolved by SDS-PAGE followed by Western blotting with antibodies specific for Chk1 (top panel) or Flag (bottom panel) (n = 4). C, D, Asynchronously growing HeLa cells were co-transfected with plasmids encoding Flag vector or Flag3Chk1, HA-ubiquitin and RNAi for 48 h and then treated with HU (20 mM) and MG132 (10 μM) for 4 h. Cell lysates were prepared and analyzed directly by Western blotting (panel C) or flag-tagged Chk1 precipitates were isolated prior to SDS-PAGE and subjected to Western blotting with antibodies specific for HA (top panel) and Flag (bottom panel) (n = 3).