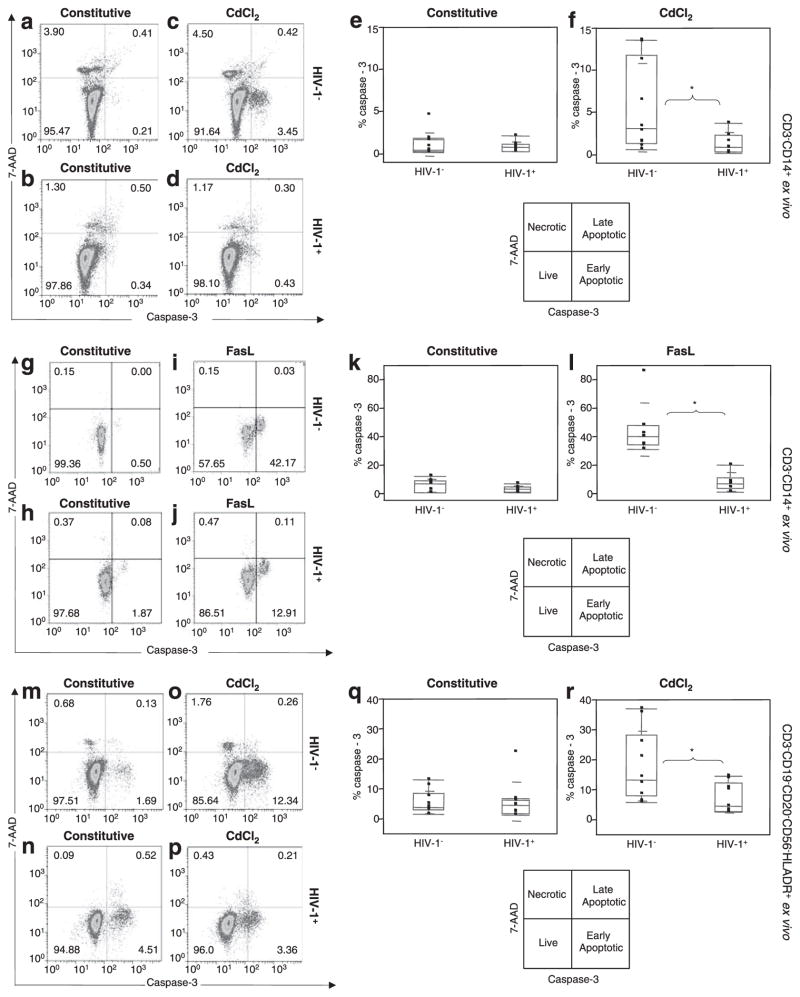
FIGURE 3.
HIV-1+ monocytes exhibit resistance to apoptosis in contrast to HIV-1+ CD4 T cells ex vivo. In contrast to CD4 T cells, no difference was found in constitutive apoptosis between control (HIV-1−) (a) and HIV-1+ (b) monocytes, but a higher CdCl2-induced apoptosis was found in HIV-1− (c) than in HIV-1+ (d) monocytes. Results represent the median ± SD for percentage of caspase-3 monocytes for constitutive (e) and for CdCl2-stimulated (f) conditions in 10 control and 9 viremic HIV-1 donors. Following FasL stimulation, no difference was found in constitutive apoptosis between control (HIV-1−) (g) and HIV-1+ (h) monocytes, but a higher FasL-induced apoptosis was noted in HIV-1− (i) than in HIV-1+ (j) monocytes. Results represent the median ± SD for percentage of caspase-3 monocytes for constitutive (k) and for FasL-stimulated (l) conditions in seven control and six viremic HIV-1 donors. Independent confirmation of results further show no difference in constitutive apoptosis between control (HIV-1−) (m) and HIV-1+ (n) myeloid cells but a higher CdCl2-induced apoptosis in control (HIV-1−) (o) than in HIV-1+ (p) myeloid cells. Results represent the median ± SD for percentage of caspase-3 in constitutive (q) and in CdCl2-stimulated (r) conditions for 10 controls and 9 viremic HIV-1 donors. *, p ≤ 0.05.