Figure 3.
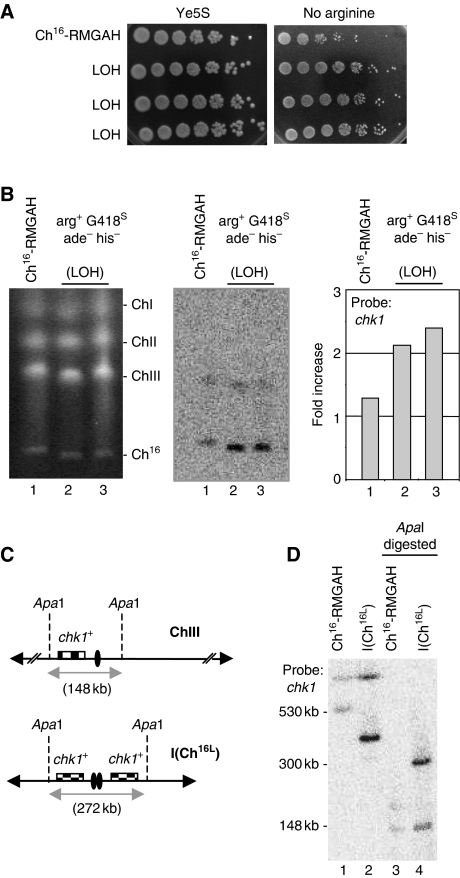
Extensive LOH arises from isochromosome formation. (A) Spot dilutions of wild-type Ch16-RMGAH (TH2130) and three individual wild-type arg+ G418S his− ade− strains (LOH) on Ye5S and EMM plus uracil, histidine, adenine and thiamine (no arginine) plates. (B) Left panel: PFGE analysis of chromosomal DNA from wild-type Ch16-RMGAH (TH2130; lane1) and individual wild-type arg+ G418S his− ade− (LOH) strains isolated after DSB induction (lanes 2 and 3). Middle panel: Southern blot of the PFGE probed with chk1. Right panel: quantification of the Southern blot indicating the fold increase over the chk1+ background present on ChIII. (C) Positions of relevant ApaI sites are indicated for the native chromosome III (ChIII; 148 kb apart), and for an isochromosome (ICh16L; ∼272 kb apart). Centromeric regions indicated by ovals. Checked boxes indicate the position of chk1. (D) Southern blot analysis of chromosomal DNA digested using ApaI and probed with chk1.