Fig. 3.
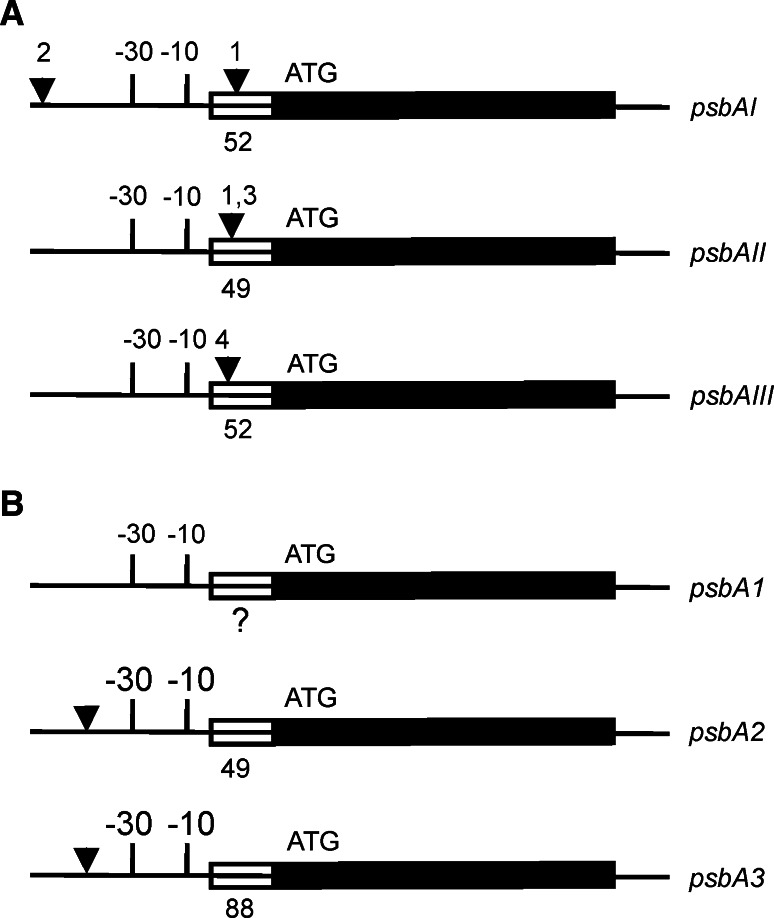
Regulatory elements of the psbA genes. a Regulatory elements of the psbAI, psbAII and psbAIII genes in Synechococcus 7942 (not in scale). The region composing the 1.2 kb transcript of each psbA gene is shown as a thick line. The coding region (starting with ATG) is marked as a solid black line and the 5′UTR as a striped line with a number below indicating the length in base pairs (bp). For each gene, the −10 and −30 regulatory elements (atypical TCTCCT in psbAI) are shown. The black triangles show the approximate binding sites for various (putative) trans-acting regulatory factors. (1) One psbAI-specific and at least one regulatory factor shared with psbAI and psbAII bind to the 5′ end of the psbAI coding region. (2) The degradation products of the D1:1 protein bind to the upstream region of the psbAI gene. (3–4) CmpR increases the expression of psbAII and psbAIII by interacting with the TTA-N7/8-TAA sequence. Other uncharacterized regulatory proteins may be involved as well, and the AT-rich region downstream from the basal elements of the psbAII gene may additionally affect the gene expression. Additional negative and positive elements upstream of the basal promoter have been identified (not shown), but the interacting trans-factors remain to be elucidated. b Regulatory elements of the psbA1, psbA2 and psbA3 genes in Synechocystis 6803 (not in scale). The region composing the 1.2 kb transcript of each psbA gene is shown as a thick line. The coding region (starting with ATG) is marked as a solid black line, and the 5′UTR as a striped line with a number below indicating the length in base pairs (bp). The transcription start site of the psbA1 gene is not known. For each gene, the −10 and −30 regulatory elements are shown. The −30 site in psbA1 differs significantly from those of psbA2 and psbA3. The black triangles show the binding sites (TTCAA-N4-TTACAA) of at least one putative transcriptional repressor, which stalls transcription of the psbA2 and psbA3 genes in the dark