Figure 5.
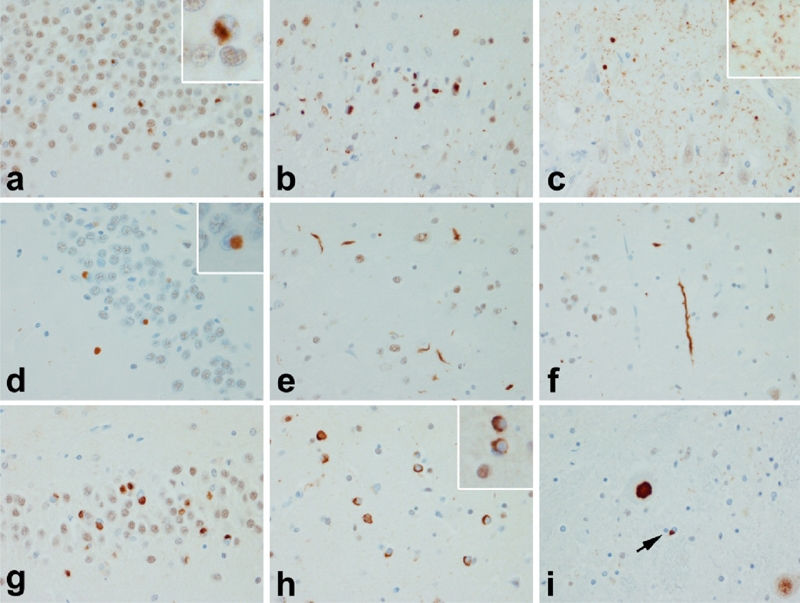
TDP-43 proteinopathies: a, b & c FTLD-TDP Type 1; d, e & f FTLD-TDP Type 2; g, h & I FTLD-TDP Type 3. Distinct patterns of TDP-43 pathology define subtypes of TDP-43 proteinopathies. In Type 1 there is widespread pathology in forebrain and hindbrain structures, with neurites and neuronal cytoplasmic inclusions (NCI) in hippocampal dentate fascia (a) and neocortex (b). A characteristic feature of many Type 1 cases is the presence of many small fine neurites in the pyramidal layer of the hippocampus (c). In Type 2 there are round dense NCI in the hippocampal dentate fascia (d) (as well as in the amygdala and basal ganglia), but predominantly long thick neurites in the cortex (e & f). The pathology is minimal in the hindbrain in Type 2. In Type 3 cases the predominant pathology is NCI with a paucity of dystrophic neurites. In addition to the hippocampus (g) and cortex (h), NCI are found in motor neurons of the brainstem and spinal cord (i). Inclusions in Type 3 are similar to those in ALS, with more widespread forebrain involvement in cases with dementia than in those with only motor neuron signs.
