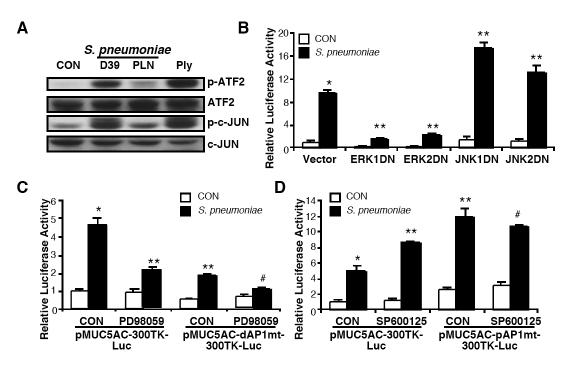
Figure 4.
Two distinct AP-1 sites in MUC5AC promoter region mediate the ERK-dependent positive and the JNK-dependent negative regulation of MUC5AC induction, respectively. A, HM3 cells were treated with S. pneumoniae strain D39, pneumolysin-deficient strain PLN, or purified pneumolysin, and expression levels of total and phosphorylated ATF-2 and c-Jun were measured by western blotting analysis. B, HM3 cells were transfected with pMUC5AC-300TK-Luc with or without DN mutants of ERK1/2 or JNK1/2, and treated with S. pneumoniae strain D39. MUC5AC transcription was measured 5 hours after S. pneumoniae or control treatment. C, HM3 cells were transfected with pMUC5AC-300TK-Luc or pMUC5AC-dAP1mt-300TK-Luc, and treated with PD98059 for 1 hour followed by S. pneumoniae strain D39 treatment. MUC5AC transcription was measured 5 hours after S. pneumoniae or control treatment. D, HM3 cells were transfected with pMUC5AC-300TK-Luc or pMUC5AC-pAP1mt-300TK-Luc, and treated with SP600125 for 1 hour followed by S. pneumoniae strain D39 treatment. MUC5AC transcription was measured 5 hours after S. pneumoniae or control treatment. Data in A are representative result from three independent experiments. The values presented in B – D are Mean ± SD (n = 3). *, p<0.05 compared with CON in vector transfected cells (B) or wild-type reporter gene transfected cells (C & D); **, p<0.05 compared with S. pneumoniae treatment in vector transfected cells (B) or wild-type reporter gene transfected cells (C & D); #, p>0.05 compared with S. pneumoniae treatment in mutant reporter gene transfected cells (C & D).