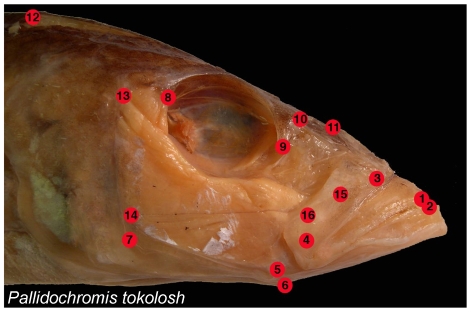
Figure 2. Anatomical landmarks examined:
1 = Tip of the anterior-most tooth on the premaxilla; 2 = Tip of the anterior-most tooth on the dentary; 3 = Maxillary-palatine joint (upper rotation point of the maxilla); 4 = Maxillary-articular joint (lower point of rotation of the maxilla); 5 = Articular-quadrate joint (lower jaw joint); 6 = Insertion of the interopercular ligament on the articular (point at which moth opening forces are applied); 7 = Posterio-ventral corner of the preopercular; 8 = Most posterio-ventral point of the eye socket; 9 = The most anterio-ventral point of the eye socket; 10 = Joint between the nasal bone and the neurocranium; 11 = Posterior tip of the ascending process of the premaxilla; 12 = Dorsal-most tip of the supraoccipital crest on the neurocranium; 13 = Most dorsal point on the origin of the A1 division of the adductor mandibulae jaw closing muscle on the preopercular; 14 = Most dorsal point on the origin of the A12 division of the adductor mandibulae jaw closing muscle on the preopercular; 15 = Insertion of the A1 division of the adductor mandibulae on the maxilla; 16 = Insertion of the A2 division of the adductor mandibulae on the articular process.