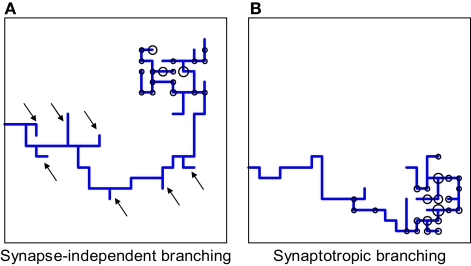
Figure 7.
Comparing synapse-independent branching and synaptotropic branching for axons. (A) If the branching is synapse-independent, new branches are formed along all segments of the arbor, both proximal and distal to the correct TZ. (B) In the case of synaptotropic branching, new branches are formed only along the arboreal segment closest to the correct TZ, and there are no erroneous branches formed along segments that are far away from its future TZ [marked by arrows in (A)]. Thus, synaptotropic branching allows for axons to reach the correct TZ using fewer branches.