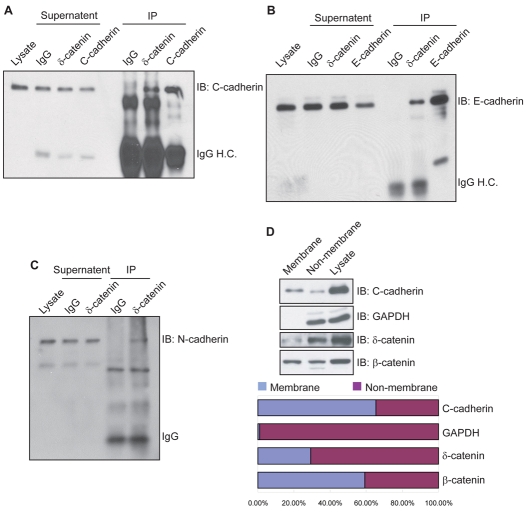
Fig. 4.
Xenopus δ-catenin associates with classical cadherins and displays a significant non-membrane-associated fraction. Endogenous δ-catenin complexes were immunoprecipitated using a C-terminus-directed antibody (1297-1314), and immunoblotted using antibodies direct against cadherins. Positive co-immunoprecipitation results suggest an association of δ-catenin with C-cadherin in gastrulating embryos (A), and with E-cadherin (B) and N-cadherin (C) in neurulation stage embryos. Immunoglobulin heavy chain (IgG H.C.) bands are included to reflect the specific versus negative control antibody input. (D) Crude membrane fractionations of gastrula embryos followed by immunoblot analyses indicate the predominant localization (∼70%) of endogenous δ-catenin within non-plasma-membrane pools. As expected, GAPDH is almost exclusively evident in the non-plasma-membrane pools. C-cadherin predominantly resides within the plasma-membrane pool (65%), with the remaining fraction likely to reflect associations with non-sedimenting vesicular stores, endoplasmic reticulum or Golgi.