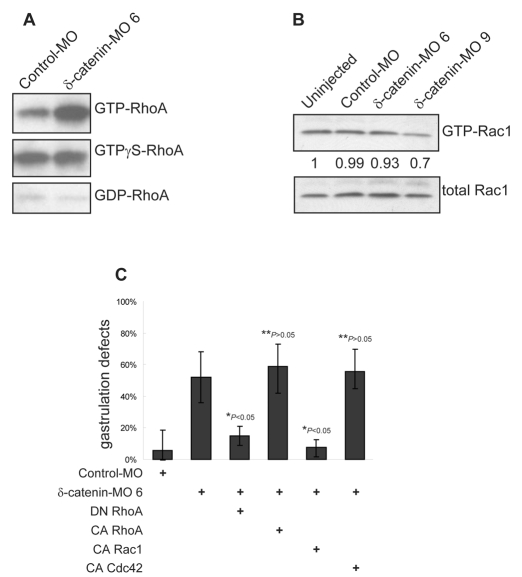
Fig. 8.
δ-catenin depletion results in activation of RhoA and inhibition of Rac1. (A) Rhotekin pull-down assays reveal strong activation of RhoA following δ-catenin depletion. (B) δ-catenin knockdown modestly reduces active Rac1 levels as measured by PBD (PAK-binding domain) affinity pull-down experiments. (C) Consistent with our biochemical evidence, a titrated dose of dominant-negative (DN) RhoA, but not constitutively active (CA) RhoA, significantly rescues δ-catenin-depletion phenotypes. Likewise, constitutively active Rac1, but not constitutively active Cdc42, rescues blastopore closure defects in δ-catenin-depleted embryos. P-values indicate statistical significance.