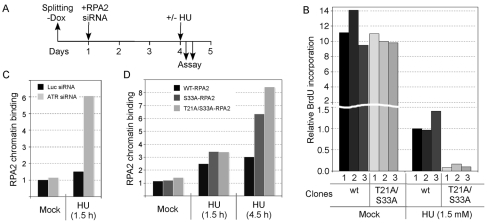
Fig. 5.
The T21A-S33A-RPA2 mutation inhibits DNA repair synthesis and increases ssDNA accumulation during replication stress. (A) Schematic indicating the steps involved in cellular RPA2 replacement. `–Dox' indicates the removal of doxycycline to cause the induction of ectopic RPA2 expression. Three U2-OS clones each that express either wt-RPA2 or a mutant RPA2 variant were invariably tested. Ectopic RPA2 was induced and, 24 hours later, the endogenous RPA2 was silenced. 3 days later, cells were either mock-treated (no stress) or treated with HU for various times and processed. (B) U2-OS clones were replaced with either wt-RPA2 or T21A-S33A-RPA2, and then either mock- or HU-treated (1.5 mM) for 4.5 hours. Cells were then incubated with BrdU and processed as described in Materials and Methods for analysis of BrdU incorporation. Approximately 500 cells were analyzed for each clone, quantitating the average BrdU signal from all cells. (C,D) U2-OS cells were transfected with siRNA molecules against luciferase (Luc; control) or ATR (C), or cloned cells replaced with either wt-, S33- or T21A-S33A-RPA2 (D). Cells were then either mock- or HU-treated (5 mM) for 1.5 or 4.5 hours (as indicated). Following extraction and fixation, cells were stained for RPA2 and imaged by epifluorescence microscopy. The average signals of retained, and hence chromatin-bound, RPA2 were determined.