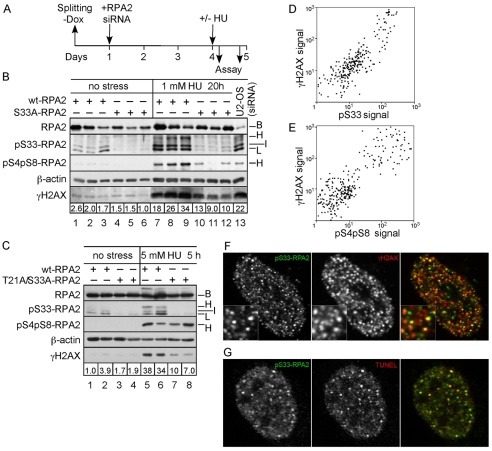
Fig. 7.
Cells replaced with the T21A/S33A-RPA2 mutant have a reduced γH2AX signal during replication stress. (A) Schematic indicating the experimental protocol. (B) Three U2-OS clones each were replaced with wt- or S33A-RPA2. At 3 days post-silencing, cells were either mock-treated or incubated with 1 mM HU for 20 hours. Lysates were then prepared and subjected to western analysis against γH2AX, RPA2 (total), S33-P-RPA2, S4-P-S8-P-RPA2 and β-actin (loading control). Also included as a control is a lysate from U2-OS cells that were silenced but not replaced (lane 13). Numbers below γH2AX panel indicate the intensity of γH2AX staining, normalized to β-actin levels. (C) Identical to panel B except that two clones each of cells replaced with wt- or T21A/S33A-RPA2 were treated with 5 mM HU for 5 hours. (D) U2-OS cells were treated with 1 mM HU for 10 hours and then fixed. Cells were stained with antibodies against S33-P-RPA2 and γH2AX. Approximately 300 cells were analyzed by immunofluorescence microscopy for the intensity of two stains, and these signals plotted against each other. (E) Similar to panel D, except that cells were treated with 5 mM HU for 5 hours and assayed for S4-P-S8-P-RPA2 and γH2AX. (F,G) Aliquots of cells described in D were stained for S33-P-RPA2 and either γH2AX (F) or a modified TUNEL assay to directly detect DNA ends (G). Cells were then imaged by immunofluorescence microscopy. The right image for each panel shows the combined staining for the two markers, with the colors of each marker indicated by the color of letters for each stain.