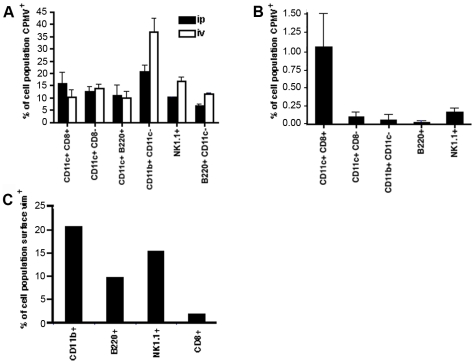
Figure 5. Quantitative analysis of CPMV uptake by different subpopulation of APCs in vivo.
(A) Groups of three C57BL/6 mice were inoculated: intraperitoneally (black columns) or intraveously (white columns) with 100 µg of CPMV-AF488. After 4 hours, spleens were removed and the cells stained to analyze the internalization of the CPMV into CD11c+/CD8α+ cells (lymphoid DCs), CD11c+/CD8α− cells (myeloid DCs), CD11c+/B220+ cells (plasmocytoid DCs), CD11c−/CD11b+ cells (macrophages), B220+/CD11c− cells (B-lymphocytes), and NK1.1+ cells (natural killer cells). After staining, the cells were fixed and analyzed by FACS. The columns represent the percentage of CPMV positive cells from each subpopulation of cells. Mice inoculated with PBS were used to subtract the background. (B) Groups of three C57BL/6 mice were inoculated by oral gavage using 1000 µg of CPMV-AF488. After 20 hours, spleens were removed and treated the same way as described above. (C) Splenocytes were isolated from C57BL/6 mice and red blood cells were removed. Dendritic cells remain in the connective tissue and do not flow through the cell strainer. Remaining cells were blocked and stained (CD11b for macrophages, B220 for B cells, NK1.1 for natural killer cells, and v4630 anti-vimentin antibody for vimentin). Cells were then fixed and analyzed by FACS.